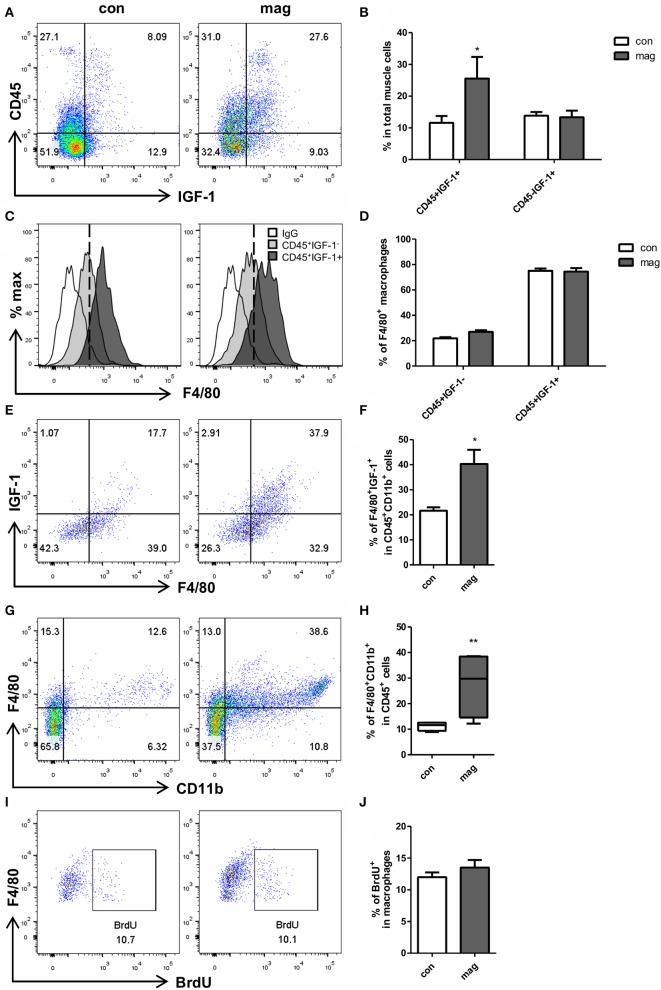
Figure 4.
Magnolol increased the infiltration of IGF-1+ macrophages into muscle tissue. Wild type mice were given vehicle (con) or 10 mg/kg magnolol (mag) intraperitoneally 3 times for a week. Single cells were isolated from TA muscle and analyzed using flow cytometry. BrdU was injected 3 h before sacrifice for proliferation assay. (A) Representative dot plots of CD45 vs. IGF-1 within total single cells from TA muscle tissues. (B) Bar graph shows the percentage of CD45+IGF-1+ and CD45− IGF-1+ populations in total cells. (C) Histograms showing the cell counts based on the F4/80 expression (white: isotype control; filled light gray: gated on CD45+IGF-1−; filled dark gray: gated on CD45+IGF-1+). (D) Percentages of F4/80+ macrophages in IGF-1+ or IGF-1− cells among the CD45+ immune cells. (E,F) Percentages of IGF-1 expressing F4/80+ macrophages measured by gating on CD45+CD11b+ cells. (G) Representative FACS plots of CD11b+F4/80+ macrophages gated on CD45+ cells in muscle tissue and (H) bar graph showing the percentage of CD11b+F4/80+ cells in CD45+ cells. (I,J) Frequency of BrdU+ proliferating populations in CD11b+F4/80+ macrophages. All graphs are presented as the mean ± SEM (n = 4). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 vs. con based on the unpaired t test. The letters for no significance were not shown.