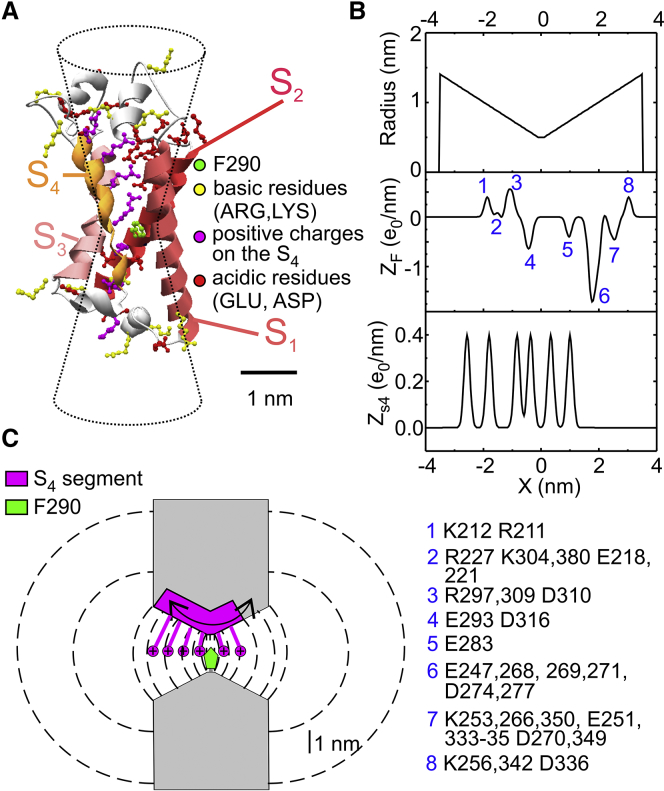
Figure 1.
(A) Model of the Shaker 3D structure obtained by homology modeling using the Kv1.2/Kv2.1 chimera structure (2R9R) as template. Gating charges on the S4 segment are in magenta, whereas negative and positive residues located in the remaining segments of the VSDs are in red and yellow, respectively. The residue F290 (homologous of F233 in the chimera channel) is in green. The hourglass-shaped drawing superimposed on the Shaker structure represents the geometry used in our model to delimit the gating pore and vestibules. (B) Profiles of the gating pore radius, the fixed charge density located in the S1–S3 region of the VSD (ZF), and the charge density on the S4 segment (ZS4), for the Shaker model structure. For symmetrical reasons, x = 0 was assumed to coincide with the center of the gating pore, where F290 is located. The blue numbers on the ZF plot and the associated legend at the bottom identify the residues contributing to the various peaks of the profile. (C) Schematics showing the geometry of the VSD assumed in our model. The S4 segment containing the six gating charges was assumed to move perpendicular to the membrane through the gating pore (0.2 nm long) and the extracellular and intracellular vestibules (each 3.4 nm long and opening with a half angle of 15°). The dashed lines represent some of the surfaces delimiting the volume elements considered in our numerical simulations (see text for details).