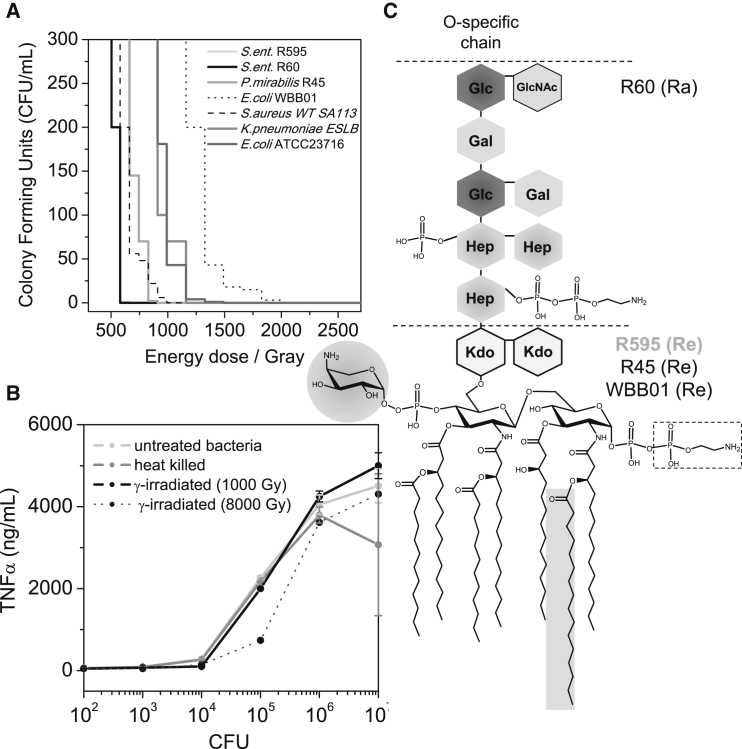
Figure 1.
Bacterial survival and mononuclear cell stimulation. (A) A total volume of 1 mL of 1.0 × 108 CFU/mL was γ-irradiated at different energy doses and then plated on LB agar. Survival curves obtained are representative for three independent experiments. (B) Stimulation of hMNCs (1.0 × 106/well) by untreated (control), heat-killed, and γ-irradiated (doses 1000 or 8000 Gy) S. enterica R60 (1.0 × 102 until 1.0 × 107 bacteria/well) cells for 1 h at 37°C. The γ-irradiation was performed at ∼5.5 Gy/min at 0°C. The mean value of the TNF-α secretion of three independent experiments is shown together with error bars representing the standard deviation (s.d.). (C) Schematic chemical structures of different LPS rough strains. The phosphate residue at the second heptose and the 2-aminoethyl diphosphate residues at the first heptose are only present in the strain R60. The LPS structures of S. enterica R595, P. mirabilis R45, and E. coli Re-mutant WBB01 differ mostly in the degree of amino-arabinose linked to the 4′-phosphate of glucosamine II (gray shaded circle), which leads to a reduction of the negative charge. 50% of the LPS R45 structure contains amino-arabinose at the carboxy group of the first 3-deoxy-D-manno-oct-2-ulosonic acid sugar. Furthermore, strain R595 has a nonstoichiometric acyloxyacyl chain C-16 in position 2 of the glucosamine I backbone. The bacterial chemotype is given in parentheses.