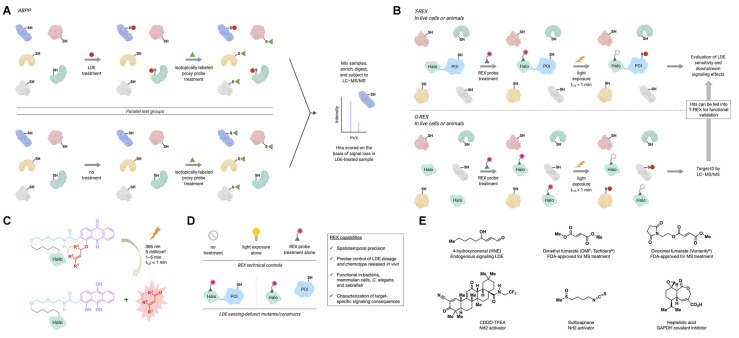
Figure 1.
Activity-based protein profiling (ABPP) and REX technologies profile lipid-derived electrophile (LDE) sensors and/or interrogate target-specific LDE signaling. (A) In ABPP, parallel test groups (typically lysates/homogenates) are first treated with the LDE of interest, or not treated (typically, DMSO control). Subsequently, both groups are treated with a broadly reactive proxy electrophile probe, which is isotopically labeled. The samples are then mixed, enriched, digested, and subjected to liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS), where loss of proxy probe labeling allows quantitative ranking of LDE modification events. (B) Top: in targetable reactive electrophiles and oxidants (T-REX), a Halo-protein of interest (POI) fusion is expressed in live cells, worms, or zebrafish. The system is then treated with a photocaged precursor to an LDE of interest (REX probe; see panel C). After removal of excess REX probe, the system is exposed to UV light (365 nm, 5 mW/cm2, 1–5 min) to liberate, in the vicinity of the POI, the LDE (in an amount maximally stoichiometric to the in vivo concentration of Halo-POI). Provided the POI is a kinetically privileged sensor (KPS) of the LDE, it will react before the LDE diffuses away. LDE-sensing ability and downstream signaling effects can then be assayed by a number of downstream procedures (Poganik et al., 2019a). Bottom: genome-wide profiling ofreactive-electrophile and -oxidant sensors (G-REX) is similar to T-REX except that G-REX involves expression of HaloTag with no POI fusion. The liberated LDE (with maximum dosage equivalent to in vivo HaloTag concentration) is captured by endogenous KPSs, which are profiled by standard quantitative proteomics (e.g., SILAC, TMT) following enrichment and digest (Poganik et al., 2019a). Hits identified by G-REX can then be fed into the T-REX workflow to validate their LDE-sensing ability and investigate target-specific consequences of LDE modification. (C) REX probes are modular, bio-inert, bind selectively and irreversibly to HaloTag in vivo, and allow rapid release of LDEs on demand. (D) Technical controls in applying REX techniques include no treatment, light exposure alone, and REX probe treatment alone. Functional controls in applying T-REX include LDE-sensing-defunct mutant POIs (by mutation of the LDE-sensing cysteine) and split constructs where Halo and POI are expressed separately (conditions under which the POI cannot be LDE-modified upon T-REX). Inset: capabilities of REX inaccessible by other tools. (E) Structures of select endogenous signaling LDEs and electrophilic drugs and inhibitors discussed in the text.