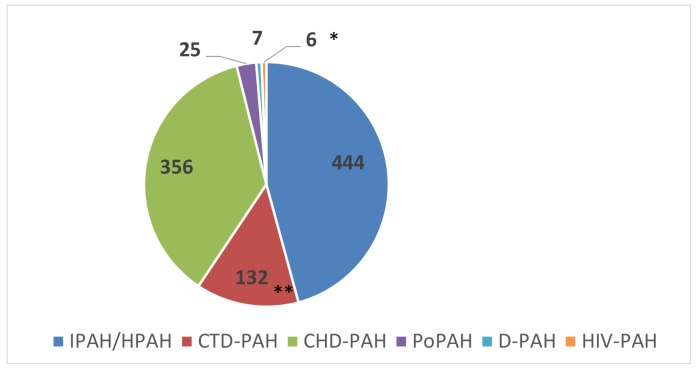
Figure 2.
Number of patients with different types of pulmonary arterial hypertension according to clinical classification. In the group of IPAH/HPAH only 12 patients were diagnosed with HPAH based on genetic testing, however PAH patients were not systematically checked for genetic background. CHD-PAH–pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) associated with congenital heart disease, CTD-PAH-PAH associated with connective tissue disease, DPAH—drugs and toxin induced PAH, HIV-PAH—PAH associated with HIV infection, HPAH—heritable PAH, IPAH—idiopathic PAH, PoPAH—PAH associated with portal hypertension. * Among patients with CTD-PAH (n = 132), the most frequent were diseases of the scleroderma spectrum (SSc-PAH, n = 63) followed by mixed connective tissue disease (n = 22), rheumatoid arthritis (n = 15), systemic lupus erythematosus (n = 13), polimiositis (n = 5), and other conditions including overlap syndromes, Sjogren′s syndrome, undifferentiated systemic rheumatic disease, and dermatomyositis (n = 14). ** In 7 patients, PAH was attributed to the use of drugs and toxins including roxadustat (n = 1), dasytinib (n = 3), interferon (n = 2), and amphetamine (n = 1).