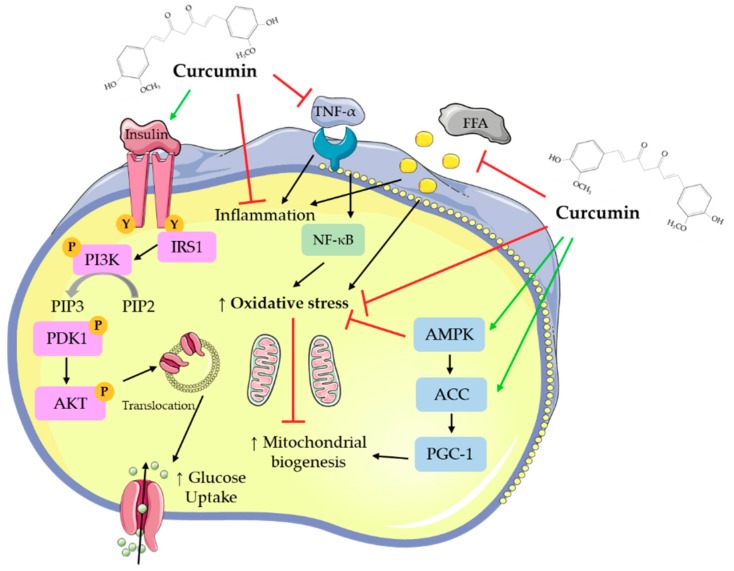
Figure 2.
Cellular effects of curcumin on muscle and fat cellular signaling molecules. The figure was created based on the data of the studies [40,41,43,44,45,46,57,67,73,97,98,101,102]. AKT: protein kinase B; PIP3: phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-triphosphate; PIP2: phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; ERK: extracellular signal-regulated kinase; PI3K: phosphoinositide 3-kinase; IRS1: insulin receptor substrate 1; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor- α; AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; ACC: acetyl-CoA carboxylase; PGC-1: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma co-activator 1; FFAs: free fatty acids.