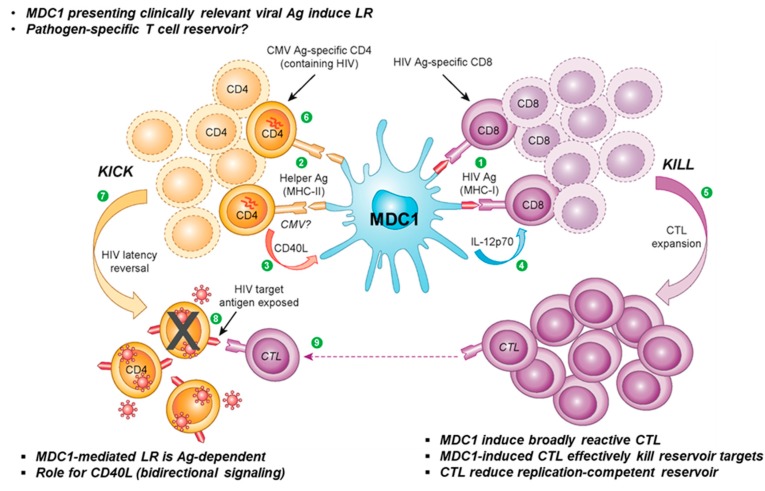
Figure 1.
Monocyte-derived DC (MDC1): the all-in-one ‘kick and kill’ tool. MDC1s induce antigen-specific CD8+ and CD4+ T cell responses through presentation of antigenic peptides in the context of (1) MHC class-I and (2) MHC class-II molecules, respectively (signal 1), along with costimulatory factors including CD80 and CD86 (not shown, signal 2). Responding CD4+ T cells subsequently provide MDC1 with the feedback hyperactivating ‘helper’ signal CD40L (3), necessary for MDC1 release of IL-12p70 (4), which then promotes expansion and differentiation of CD8+ human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1)-specific effector cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) (5). Activation of CMV and HIV antigen-responsive CD4+ T cells harboring latent HIV-1 (6) results in HIV latency reversal (7), with HIV-1 proteins being transcribed and expressed as surface antigen (8). As a result, exposed infected cells harboring replication-competent provirus are targeted for elimination by HIV-specific CTLs (9).