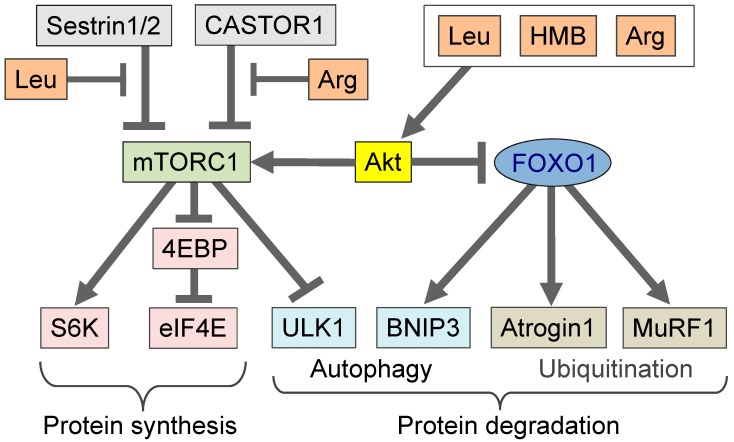
Figure 2.
mTORC1 is activated by amino acids, such as leucine, HMB, and arginine. mTORC1 phosphorylates substrates, such as 4EBP and S6K, and increases protein synthesis. Moreover, in the presence of these amino acids, mTORC1 suppresses starvation signals, such as autophagy. Amino acids (leucine, HMB, and arginine) can activate Akt, leading to mTORC1 activation and FOXO1 suppression [28,34,35,36]. FOXO1 is a transcription factor that induces muscle atrophy. Suppression of FOXO1 transcriptional activity leads to decreased autophagy. Leucine interacts with Sestrin 1 or Sestrin 2 [5,32], and arginine interacts with CASTOR1 and activates mTORC1 [33]. The nature of the molecules involved in the amino acid-mediated pathway (e.g., the differences among leucine, HMB, and arginine) warrants further clarification. Leu, leucine; HMB, β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate; Arg, arginine; mTORC1, mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1; CASTOR1, cytosolic arginine sensor for mTORC1 subunit 1; FOXO1, forkhead box protein O1; S6K, S6 kinase; eIF4E, eukaryotic initiation factor 4E; 4EBP, eIF4E-binding protein; ULK1, unc-51 like autophagy activating kinase; BNIP3, Bcl-2 19 kDa interacting protein 3; MuRF1, muscle RING-finger protein-1.