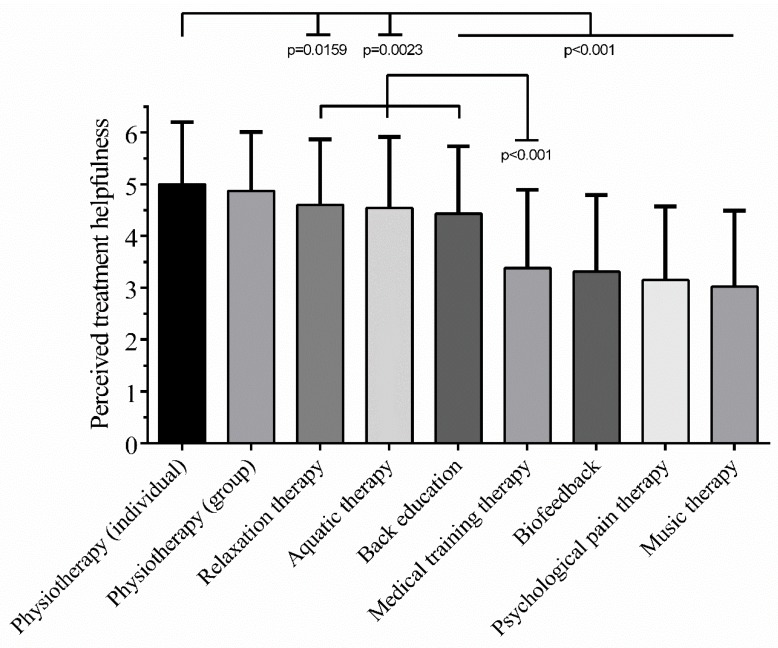
Figure 2.
Mean perceived treatment helpfulness. Mean perceived helpfulness differs significantly between treatment modalities of the multidisciplinary pain management program (Analysis of variance (ANOVA): p < 0.001). Mean helpfulness ratings (±SD) ranged from 5 (±1.2) for individually-delivered physiotherapy to 3.02 (±1.47) for music therapy. Highly significant differences were observed between individually-delivered physiotherapy and back education, medical training therapy, biofeedback, psychological pain therapy as well as music therapy (Tukey’s multiple comparison: p < 0.001). Moreover, relaxation therapy, aquatic therapy and back education were perceived to be significantly more helpful than medical training therapy (Tukey’s multiple comparison: p < 0.001). Table 1 of the program (1 = not at all helpful, 2 = I don’t know, 3 = slightly helpful, 4 = moderately helpful, 5 = very helpful, 6 = extremely helpful). Data is presented as mean ± standard deviation.