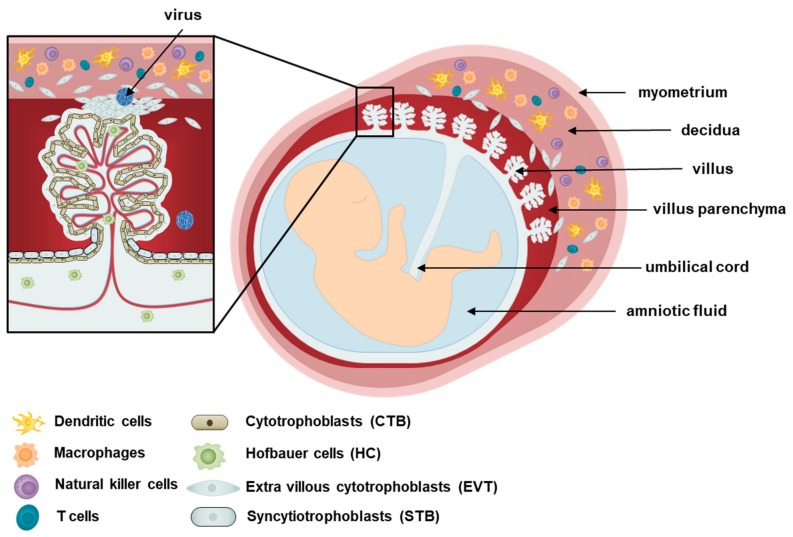
Figure 1.
Cells of the placenta. A schematic diagram of the human placenta during pregnancy is shown. The human placenta contains three main types of epithelial trophoblasts: cytotrophoblasts (CTBs), syncytiotrophoblasts (STBs), and extravillous trophoblasts (EVTs). The CTBs are mononuclear cells at the fetal interface that eventually differentiate via cell-to-cell fusion into STBs. The STB layer is a multinucleated structure that covers the entire surface of the villous tree throughout pregnancy that is bathed in maternal blood, and mediate nutrient and gas exchange between mother and fetus. Hofbauer cells (HC), macrophages of fetal origin, are found in the intervillous spaces, while EVTs migrates from the chorionic villi, invades into the uterine wall, and remodels maternal spiral arteries to facilitate blood supply of the placental unit. In addition to the EVTs, the decidual compartment also includes maternal immune cells (eg, decidual dendritic cells, macrophages, natural killer cells and T cells) and stromal cells. EVT, extravillous cytotrophoblasts; CTB, cytotrophoblasts; HC, Hofbauer cells; STB, syncytiotrophoblasts.