Figure 3.
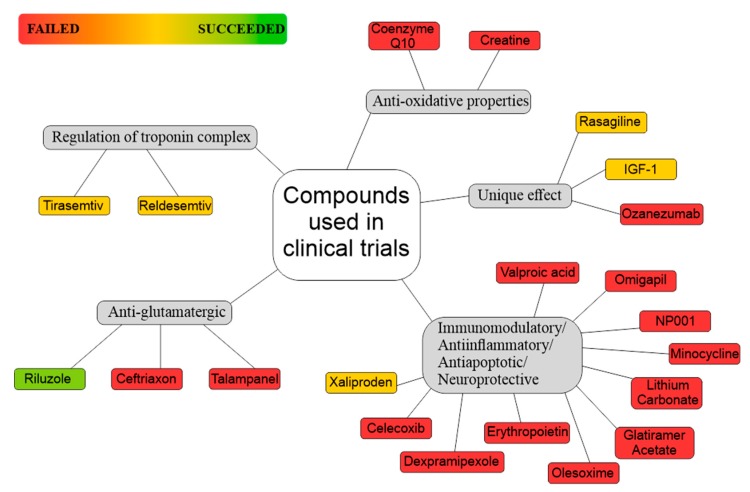
Compounds were divided into groups according to their effect, as described in clinical studies. In the category of anti-glutamatergic both Ceftriaxone [286] and Talampanel [287] failed. Another category of drugs are compounds that are thought to have anti-oxidative properties. Both Coenzyme Q10 [288,289] and Creatine [290,291,292,293,294] have failed to demonstrate clinical efficacy. Tirasemtiv and Reldesemtiv are able to regulate the release of calcium from the regulatory troponin complex and thus sensitize the muscle to calcium. Several trials assessed the efficacy of Tirasemtiv in human ALS patients. From all the studies [295,296,297,298], only one [298] managed to show statistical significance on two out of five secondary endpoints. Based on the results, a large-scale follow up study was launched but failed to demonstrate efficacy in all of its endpoints [299]. Efficacy of Reldesemtiv was assessed in a single Phase II trial. Although, this trial failed in its primary endpoint for all dose groups, patients showed a non-significant 27% reduction of decline in SVC. Moreover, all groups compared to the placebo, showed a significant 25% change in ALSFRS-R slope [300]. Most compounds used, are believed to have either immunomodulatory/anti-inflammatory/antiapoptotic and/or neuroprotective properties. Most of these compounds failed to demonstrate statistical significance in all of the studies´ endpoints. Celecoxib—[301], as part of a combined treatment with Creatine [302], Dexpramipexole [286,303], Erythropoietin [304,305], Glatiramer Acetate [306,307], Lithium Carbonate [308,309,310,311], Minocycline ([312,313,314] as part of a combined treatment with Creatine [302]), NP001 [315,316], Olesoxime [317], Omigapil (TCH-346) [318], and Valproic acid [319]. Xaliproden has managed to succeed in 1 out of 8 endpoints in one of two trials [320], however, both trials failed on their primary endpoints [320,321]. Trials of two compounds—Acthar gel (released in press in 2016) and Pioglitazone [322], were prematurely terminated due to potential risk to patients (Acthar gel) and futility (Pioglitazone). Other drugs are considered to have unique effects among the compounds assessed. Trials of Ozanezumab have failed to show clinical efficacy [323]. Another compound tested, insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), has failed to demonstrate clinical efficacy in three separate trials [324,325,326], even though one of the studies [325] succeeded in three out of three of its secondary endpoints. Another compound, Rasagiline, failed to show clinical efficacy in a single trial [327], however, post-hoc analysis has revealed a significant reduction of ALS progression in patients with an initial ALSFRS-R slope greater than one (patients with faster ALS progression).