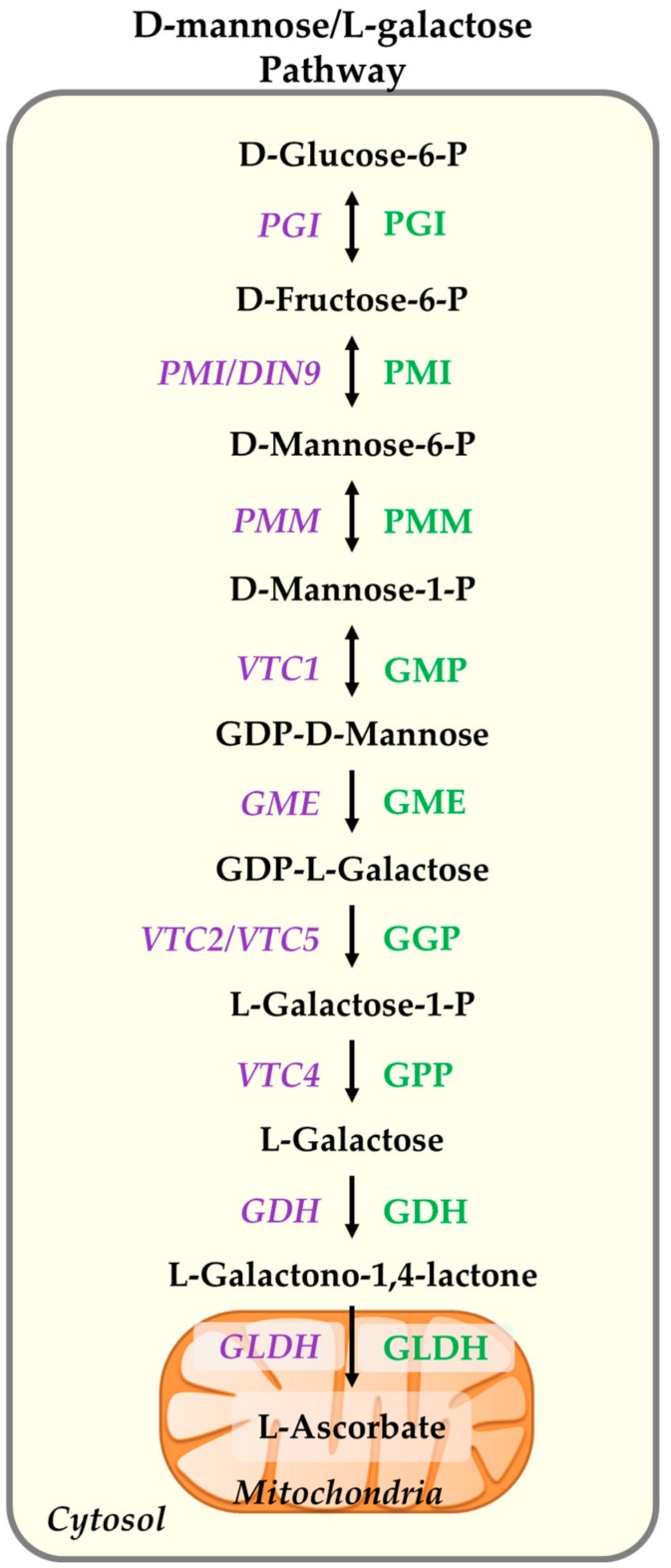
Figure 1.
D-Mannose/L-Galactose pathway of ascorbate biosynthesis in plants. The genes of the pathway are highlighted in purple and written in italics. The enzymes are highlighted in green. Phosphoglucose isomerase (PGI), phosphomannose isomerase (PMI), and phosphomannomutase (PMM) are responsible for the conversion of D-glucose-6-P to D-mannose-1-P, the direct precursor of GDP-D-mannose pyrophosphorylase (GMP), the first committed enzyme of the pathway encoded by VTC1. GDP-mannose-3′-5′-epimerase (GME), GDP-L-galactose transferase (GGP), L-galactose-1-phosphate phosphatase (GPP), L-galactose dehydrogenase (GDH), and L-galactono-1,4-lactone dehydrogenase (GLDH) are the next enzymes of the pathway. GGP is the key enzyme of the pathway encoded by VTC2 and VTC5 paralogs. This enzyme undergoes feedback regulation by ascorbate pool size. GLDH is located in the intermembrane of mitochondria and is connected to the mitochondria respiratory chain.