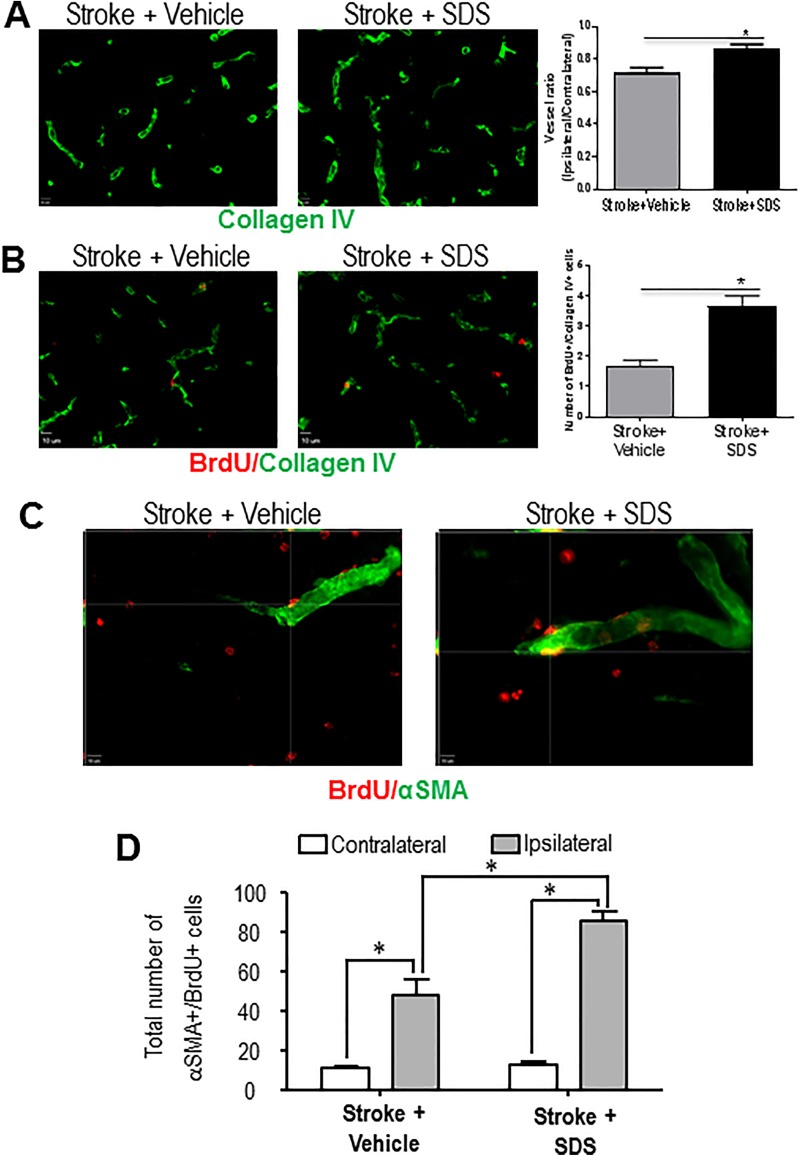
Fig. 4.
Enhanced angiogenesis and collaterogenesis by sodium danshensu.
(A) Representative images of vascular density in the peri-infarction cortex of vehicle control mice and SDS-treated mice at 14 days after stroke. (B) Endothelial cell proliferation was revealed by co-staining with collagen IV and BrdU. At 14 days after stroke, more BrdU-positive endothelial cells were seen in SDS-treated mice compared with vehicle control mice. Vessel ratio and BrdU-positive endothelial cells in the peri-ischemic cortex at 14 days after MCAO for each group were quantified. Administration of SDS significantly increased vascular density and endothelial cell proliferation 14 days after focal cortical infarction. n = 6 animals in each group. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. * P < 0.05 compared with vehicle control group. (C) Enhanced arteriogenesis by SDS. Colocalization of the smooth muscle cell marker αSMA (green) and the proliferation marker BrdU (red) in the peri-infarct region was examined 21 days after stroke. In SDS-treated mice, there were more both αSMA- and BrdU-positive cells compared with vehicle control mice. (D) Cell count was performed in six randomly chosen fields in the peri-infarct region; six regions per section. The total number of cells in six sections was summarized for each animal. Cell counts showed increased number of αSMA-/BrdU-positive cells in SDS-treated mice compared with vehicle control mice. n = 5 animals in each group. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. * P < 0.05 compared with vehicle control group. SDS: sodium danshensu; BrdU: 5-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine; MCAO: middle cerebral artery occlusion; SEM: standard error of the mean; αSMA: alpha smooth muscle actin.