Fig. 8.
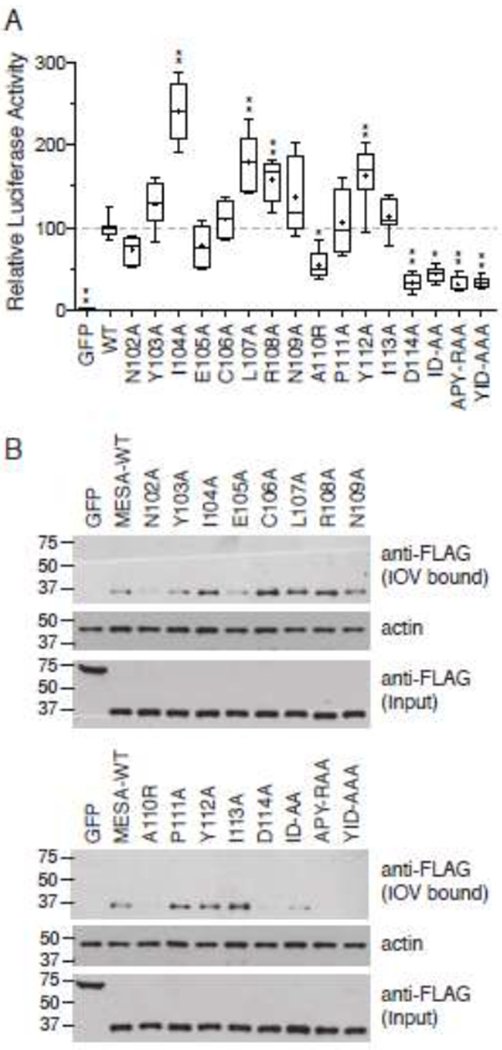
Amino acid substitutions in the MESA MEC motif disrupt binding to ankyrin.
A. Split-luciferase assay. The 12 single amino acid substitutions described in Fig. 6 were in vitro translated in wheat germ extracts as fusions to C-Fluc and tested for their interaction with N-FLuc-tagged ankyrin fragment 3 in the split-luciferase assay. Assays were initiated by addition of N-FLuc-ankyrin to samples containing C-FLuc-MESA MEC construct and luciferase substrate in binding buffer. The graph shows the mean luciferase activity (± S.D.) derived by subtracting the initial luciferase value from the third measurement (see Supplementary Fig. 3 for relative luciferase activity versus time for each sample) and normalizing the data to wild type MESA MEC, which was set to 100 (n = 8, from three independent experiments). Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons to wild type MESA MEC motif using Graphpad Prism 6 software. * p value ≤ 0.01, ** p value ≤ 0.001, *** p value ≤ 0.0001.
B. IOV binding. C-FLuc-MESA MEC motif mutants were tested for binding to erythrocyte IOVs as described in the legend to Fig. 6. Upper blot shows a western blot analysis of IOV-bound 3X-FLAG and C-FLuc-tagged MESA MEC mutants; middle blot, erythrocyte actin, which serves as a loading control for the amount of IOVs present in each sample; lower blot, amount of C-FLuc construct added to each IOV-binding reaction.
