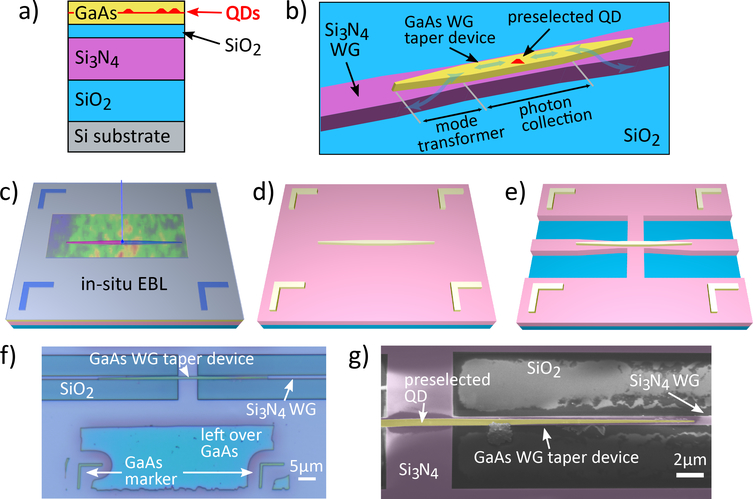
Figure 1:
a) Schematic layout of the wafer-bonded sample stack. b) Schematic GaAs-Si3N4 device design: The preselected InAs QD is hosted in a GaAs nanowaveguide that collects the QD’s emission. The emission is then coupled into the Si3N4-SiO2 WG using mode transformers. c) - e): Visualization of key sample fabrication steps: c) in situ EBL of a GaAs nanowaveguide pattern and markers aligned to a QD which was preselected using low temperature CL spectroscopy. d) GaAs nanowaveguide and markers on Si3N4 after etching the GaAs patterns and removing excess GaAs. e) fully-fabricated GaAs-Si3N4-SiO2 WG device. f) false-color optical micrograph of fully-fabricated device QD 1. g) false-color SEM image of device QD 1, showing the GaAs WG taper (yellow) and the Si3N4 WG (pink).