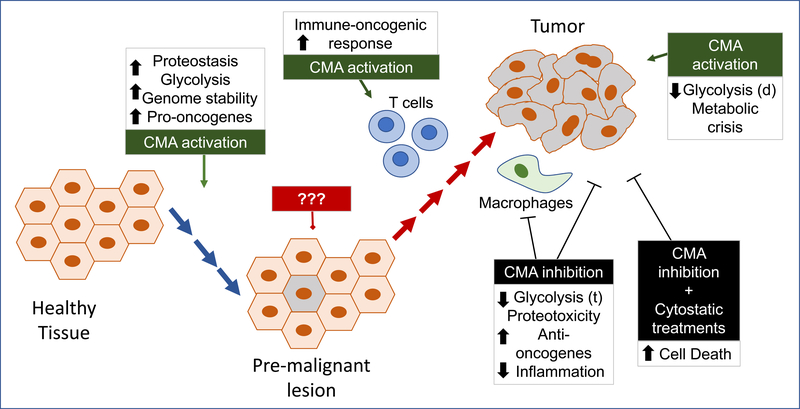
Figure 3. CMA targeting in cancer prevention and treatment.
Before malignant transformation maintaining fully functional CMA should help preserving its anti-oncogenic function. ??? denotes that experimental evidence is lacking to support value of targeting CMA in the pre-malignant lesion (before or at the moment that CMA gets upregulated), but systemic activation of CMA may help boosting the T cell mediated immune-oncogenic response. Once the tumor is formed, inhibition of CMA in tumor cells and tumor-associated macrophages has been shown to reduce tumor growth and to induced tumor death both alone or in combination with other anti-oncogenic interventions to prevent cancer cell resistance. Active upregulation of CMA has also shown effective in inducing cancer cell death in specific conditions combining inhibition of macroautophagy and metabolic stress. Boxes summarize the main cellular processes affected by the CMA-targeting intervention at each stage. (t): transcription; (d): degradation.