Fig. 2. Effects of bcsG variants on the expression of the cellulose synthase subunit BcsA and cellulose production.
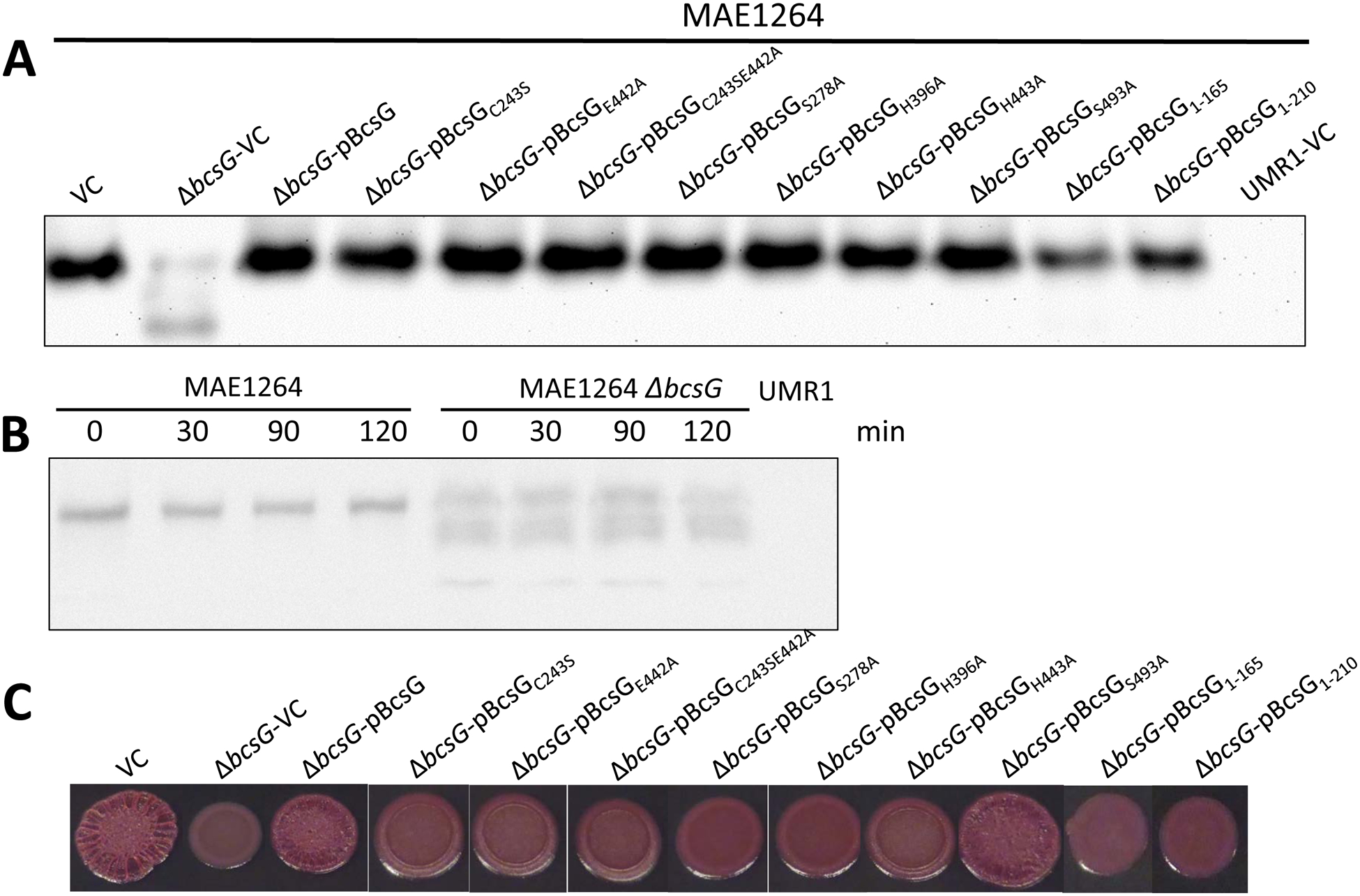
A. Expression of BcsA-3xFLAG in S. typhimurium strain MAE1264 (bcsG+ [5]) and its ΔbcsG mutant upon overexpression of bcsG and its variants. VC, pBcsG, pBcsG1–210, and pBcsGS278A are as in Fig. 1. pBcsGC243S, pBcsGE442A, pBcsGC243SE442A, pBcsGS278A, pBcsGH396A, pBcsGH443A, and pBcsGS493A are bcsG variants with mutations in predicted active site residues of the AlkP superfamily cloned in pBAD30 with a C-terminal 8x-His tag. Strain UMR1 with plasmid pBAD30 (UMR1-VC) without the 3xFLAG tag was used as a negative control. All samples contained equal amounts of cell extracts as judged by Coomassie staining.
B. Stability of chromosomally encoded BcsA in the presence (MAE1264) and the absence of bcsG. After translation was inhibited with chloramphenicol, the amount of the 3xFLAG-tagged BcsA subunit was quantified using anti-FLAG antibodies at indicated time points. Strain UMR1 without the 3xFLAG tag was the negative control. Owing to the lower expression of BcsA in the ΔbcsG mutant, 10-fold higher amounts of its cell extract than those for MAE1264 were applied on the gel.
C. Pdar colony morphotype (cellulose biosynthesis) of strains listed in panel A. Despite similar levels of the BcsA subunit (panel A), the wild-type (VC) level of cellulose production could only be observed upon overexpression of the wild-type BcsG or the BcsGS493A mutant. Cells were grown on CR salt-free LB agar plates for 24 h at 28 °C.
