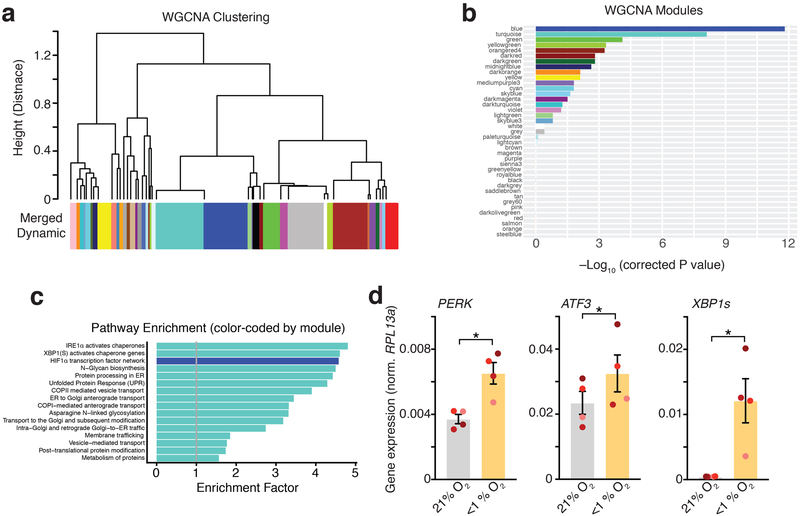
Extended Data Fig. 4. WGCNA analysis and qPCR validation.
(a) Hierarchical clustering of WGCNA modules identified in the RNA-seq data. Clustering is based on the module eigengenes (‘average’ expression profile of all module genes. The turquoise and blue modules are very similar in overall eigengene expression pattern. (b) Statistical significance for correlation of each module with low O2 exposure (bars are labeled by the color of the modules). The blue and turquoise modules are highly associated with exposure (FDR ≤ 0.05). (c) Enrichment for pathways in the turquoise and blue modules (bars are labeled by the color of the modules in which they are enriched). Only pathways with Bonferroni-corrected FDR < 1 x 10-4 are shown. (d) Validation by qPCR of the UPR-related genes PERK (two-tailed paired t-test, *P= 0.03), ATF3 (two-tailed paired t-test, *P= 0.03), XBP1s (two-tailed paired t-test, *P= 0.04), which were identified in the RNA-seq (n= 4 hiPS cell lines; each line is shown in a different color; expression normalized to the RPL13a housekeeping gene). Data are mean ± s.e.m., individual values are indicated by dots.