Figure 2.
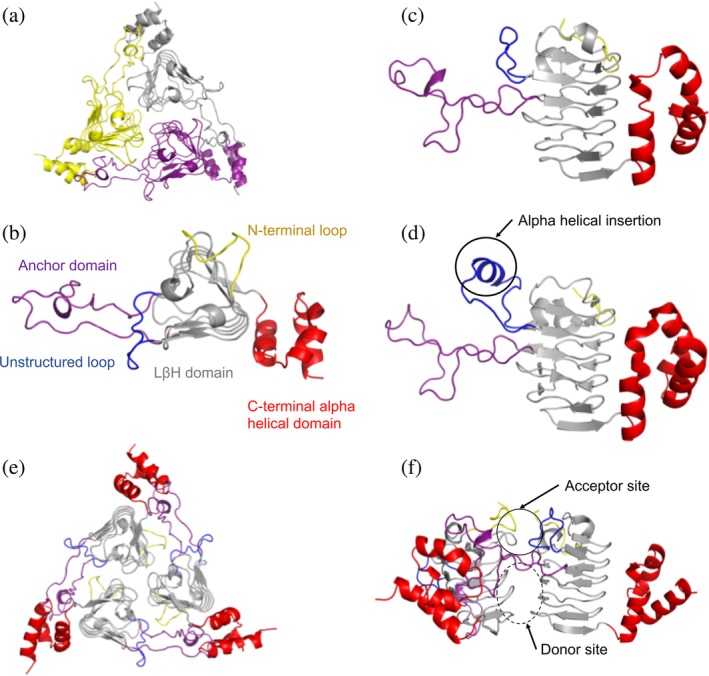
Structure and domain organization of VcCAT, VvCAT, and AfCAT proteins. (a) All three proteins were crystallized as homotrimers. A representative VcCAT structure (PDB ID: 6PUA) is shown with each monomer of the trimer highlighted in different colors. (b) Top view of domains found in each protein monomer; VcCAT structure is used as the representative. The first 10 residues of the N‐terminus are highlighted in yellow, the left‐handed beta‐helix (LBH) core is shown in gray, an unstructured loop (residues 43–54) is highlighted in blue, the anchor domain (residues 71–108) is highlighted in purple, and the C‐terminal alpha helical domain (residues 163–209) is in red. (c) Side view of domains of the VcCAT and VvCAT monomers. Colors are the same as panel B. (d) Side view of domains of the AfCAT (PDB ID: 5UX9) protein. Colors are the same as panel B. The alpha helical insertion unique to the AfCAT protein is circled. (e) Homotrimer of the VcCAT protein with domains highlighted as indicated in Panel B. (f). The interface of two monomers of the VcCAT protein that create the active site. The acceptor site and donor site are circled. All figures were prepared using PyMOL and Microsoft PowerPoint
