Figure 3.
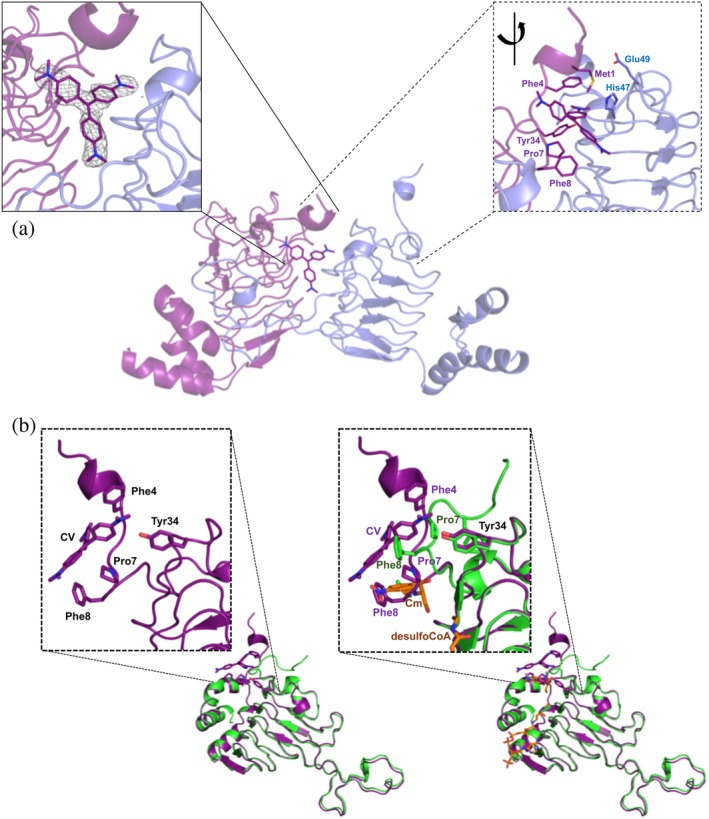
VcCAT structure in the presence of crystal violet. (a) Crystal violet binding site at dimer interface (PDB ID: 6PUB). The VcCAT structure is a trimer, but only two monomers are shown for clarity (one monomer is colored purple and the other is colored slate blue). Crystal violet is shown as purple sticks with its nitrogens in dark blue. Two views of the crystal violet binding site are shown: The left box with solid lines shows the F o weighted omit map in grey mesh surrounding the crystal violet molecule drawn at a contour level of 1.2σ. The right box with dashed lines shows a rotated view of the dimer interface with key residues of the binding site labeled and shown as sticks. (b) Comparison of VcCAT (PDB ID: 6PUA) (green) and VcCAT‐CV (PDB ID: 6PUB) (purple) structures. The ligand binding mode of crystal violet (CV) in the 6PUB structure is shown in the left panel, and the right panel shows the overlay of 6PUB and 6PUA structures. Chloramphenicol (Cm) and desulfocoenzyme A (desulfoCoA) are shown in orange and are modeled from the structure of the xenobiotic acetyltransferase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PDB ID: 2XAT). The secondary structures of each crystal structure were defined using Stride (http://webclu.bio.wzw.tum.de/stride/) and altered manually in PyMOL. All figures were prepared using PyMOL and Microsoft PowerPoint
