Figure 6 |. Model depicting the mechanism of CSPα oligomerization in ANCL and its alleviation by Fe-chelators.
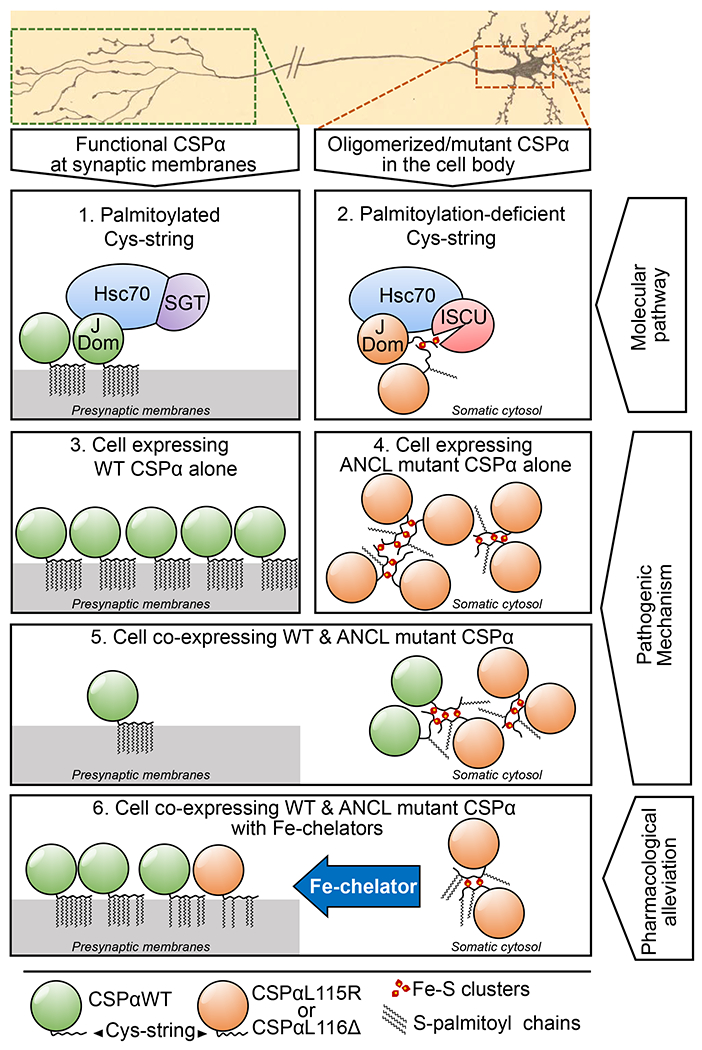
CSPαWT is heavily palmitoylated, allowing its localization to presynaptic membranes (panel 1), where it forms a functional chaperone complex with Hsc70 and SGT; which chaperones synaptic SNARE SNAP-25. The ANCL mutants CSPαL115R and CSPαL116Δ are inefficiently palmitoylated, and mislocalized away from synapses, where mutant CSPα’s J-domain (J Dom) recruits a CIA complex containing Hsc70, and ISCU – an Fe-S cluster transferring protein (panel 2). This molecular interaction leads to pathogenic oligomers of mutant CSPα: CSPαWT expressed alone is not oligomerized beyond its native homodimerization (panel 3), while the loss of palmitoylation in the ANCL mutants CSPαL115R and CSPαL116Δ accompanies ectopic binding of their reactive Cys-strings to Fe-S clusters, cross-linking the mutant CSPα molecules into oligomers. These oligomers mainly reside away from the synapse, causing loss of CSPα’s chaperone function at the synapse (panel 4). In the CSPαL115R or CSPαL116Δ heterozygous cells, mutant CSPα is able to recruit CSPαWT into oligomers, leading to less than hemizygous level of CSPα function at the synapse (panel 5). Iron-chelator treatment leads to reduction in the Fe-S cluster-bound oligomers, allowing improved CSPα function at the synapse (panel 6). This increase in functional CSPα leads to partial alleviation of the downstream SNAP-25 instability and lipofuscin accumulation phenotypes.
