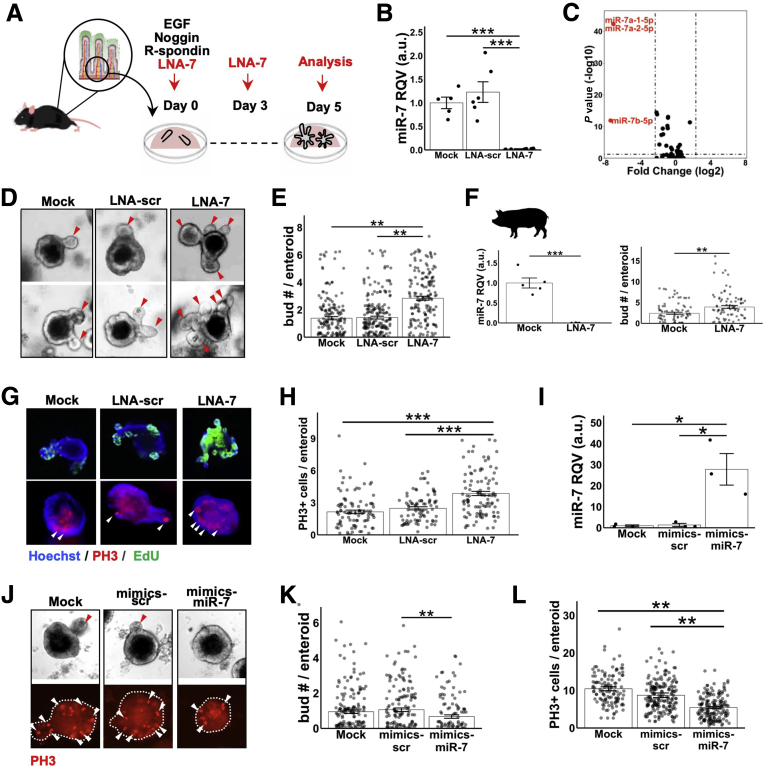
Figure 3.
MiR-7 controls intestinal epithelial growth ex vivo. (A) Experimental design for testing the effect of miR-7 suppression in enteroid culture established from C57BL/6 WT mouse jejunum. (B) RT-qPCR data showing effective suppression of miR-7 expression by LNA-7 treatments in mouse enteroids compared with mock (no treatment) and LNA-scr control (n = 5–6 wells per condition pooled from 2 independent experiments). (C) Small RNA-seq followed by differential expression analysis showing highly robust and specific suppression of all the miR-7 family members in the enteroids treated with LNA-7 compared with LNA-scr (LNA-7, n = 6; LNA-scr, n = 5). (D) Representative bright field images of enteroids treated with mock, LNA-scr, and LNA-7. (E) Bar graph depicting average number of buds per enteroid in the indicated treatment groups. Data were pooled from 3 independent experiments (mock, n = 174 enteroids; LNA-scr, n = 214 enteroids; LNA-7, n = 163 enteroids). (F) The left panel shows RT-qPCR data showing effective suppression of miR-7 by LNA-7 (n = 5 wells/condition) in porcine enteroids. The right panel shows bar graph depicting average number of buds per porcine enteroid in the indicated treatment groups. Enteroids were pooled from 5 independent experiments (mock, n = 83; LNA-7, n = 86 enteroids). (G) Representative images of mouse enteroids showing whole-mount staining signal for EdU (green; top) and PH3 (red; bottom). (H) Bar graph depicting average number of PH3+ cells per enteroid. All of the enteroids across multiple wells were examined (mock, n = 100 enteroids; LNA-scr, n = 83 enteroids; LNA-7, n = 106 enteroids). (I) RT-qPCR data showing effective increase in miR-7 levels in mouse enteroids treated with mimics of miR-7 (mimics-miR-7) compared with mock (no treatment) and mimics-scramble (mimics-scr) (n = 3 wells per group). (J) Representative brightfield images of wild-type mouse enteroids (top) and whole-mount staining signal for PH3 (red; bottom) in the indicated treatments. (K) Quantification of the average number of buds per enteroid in the indicated treatments. Enteroids per treatment group were pooled from multiple wells for quantification (mock, n = 175; mimics-scr, n = 168; mimics-miR-7, n = 116). (L) Quantification of the average number of PH3+ cells per enteroid in the indicated treatments. All of the enteroids across multiple wells were examined (mock, n = 123 enteroids; mimics-scr, n = 190 enteroids; mimics-miR-7, n = 165 enteroids). * P < .05, ** P < .01 and *** P < .001 by 2-tailed Student t test. RQV, relative quantitative value.