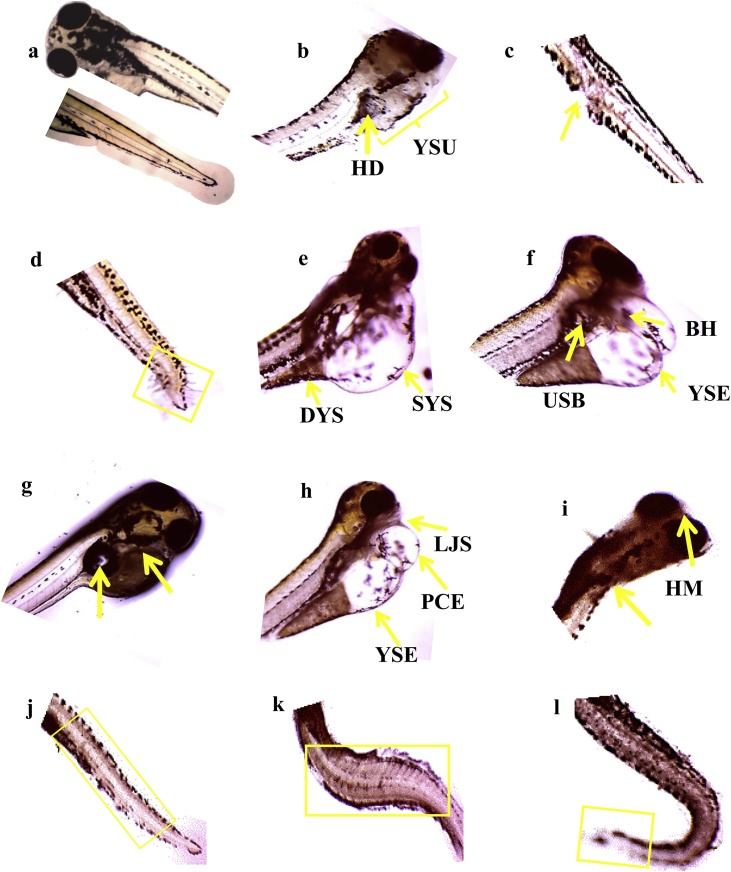
Fig. 4.
Deformity observed in larvae of zebrafish exposed to sumithion. a. normal larvae; b. yolk sac ulceration (YSU) and heart damage (HD) after 36 h of exposure to 0.4 mg L−1 of sumithion; c. lesion/ulceration of caudal region after 36 h of exposure to 0.8 mg L−1 of sumithion; d. end tail shortening and malformation after 36 h of exposure to 0.8 mg L−1 of sumithion; e. swollen yolk sac (SYS), swollen and discontinuous yolk sac (DYS) after 48 h of exposure to 1.6 mg L−1 of sumithion; f. uninflated swim bladder (USB), yolk sac edema (YSE), blood hemorrhage (BH) after 60 h of exposure to 0.8 mg L−1 of sumithion; g. black pigmentation on yolk sac and unlooped heart after 72 h of exposure to 0.8 mg L−1 of sumithion; h. pericardial sac edema (PSE), lower jaw shortening (LJS), yolk sac edema (YSE) after 60 h of exposure to 1.6 mg L−1 of sumithion; i. head malformation (HM) and spine scoliosis after 84 h of exposure to 0.4 mg L−1 of sumithion; J; notochord abnormalities after 84 h of exposure to 0.8 mg L−1 of sumithion; k. lordosis and irregular caudal region after 96 h of exposure to 0.4 mg L−1 of sumithion; l. deformed posterior part of body and tail ulceration after 96 h of exposure to 0.4 mg L−1 of sumithion.