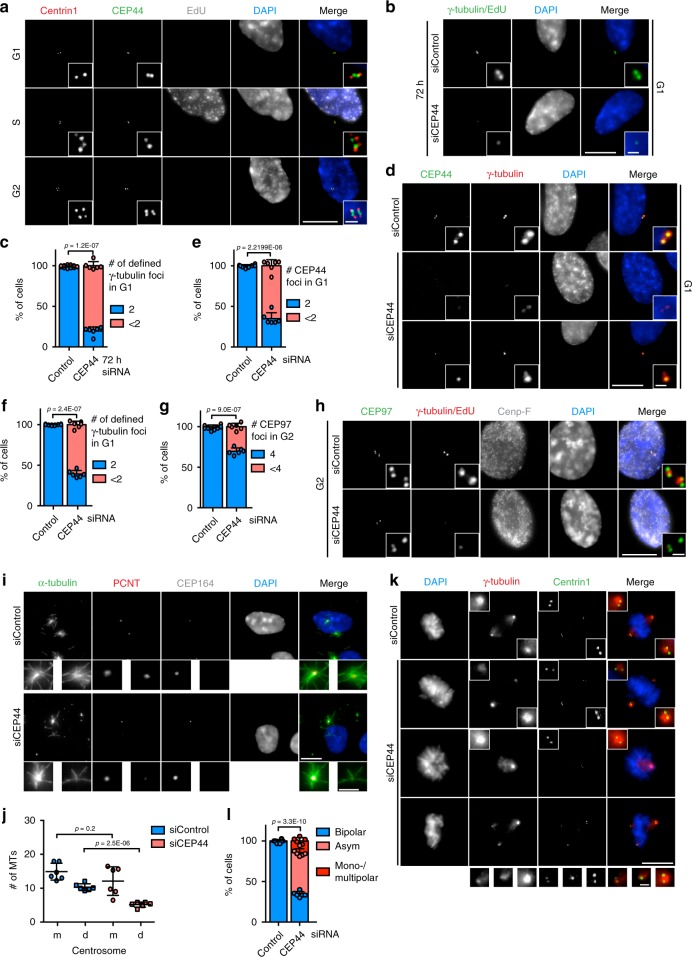
Fig. 1. CEP44 is a centriolar protein necessary for the CCC mechanism.
a IF of cycling RPE1 cells showing that CEP44 binds to the new dCs during G2. While S phase cells were detected by EdU stain, G1 and G2 cells were discerned by the lack of EdU stain and the number of centrin1 signals (centrioles). b IF of cells after 72 h of depletion. In the siCEP44 sample (lower panel) G1 cells contained less centrosomes as judged by the number of γ-tubulin foci (Cenp-F in Supplementary Fig. 1b). c Quantification of b. 80.4 ± 5.0% of G1 cells contained <2 centrosomes. d IF of 60 h siRNA treated RPE1 cells in G1. While the G1 control cells contained 2 defined PCM foci (γ-tubulin) accompanied by equal number of CEP44 foci, in the siCEP44 sample the loss of CEP44 correlated with inefficient PCM (γ-tubulin) recruitment to only one (bottom panel) or both centrosomes (middle panel) (Cenp-F, Supplementary Fig. 1g). e Quantification of CEP44 loss in d. 65.1 ± 7.3% of G1 cells contained <2 CEP44 foci. f Quantification of γ-tubulin defined foci in d. 60.7 ± 4.2% of G1 cells contained <2 defined γ-tubulin signals. g, h G2 CEP44-depleted cells after 60 h of CEP44 depletion showed a mild centriole duplication defect as judged by the counting of CEP97 foci (<4). g Quantification of h. 30.3 ± 4.1% of CEP44-depleted cells contained <4 centrioles. i MT regrowth assay in RPE1 C-Nap1 KO cells. The non-converted daughter centrosome without CEP164 staining regrew lower numbers of MTs (5.1 ± 2.7 MTs/centrosome) than the siControl daughter centrosomes (10.3 ± 3.0 MTs/centrosome) upon cold treatment and MT regrowth. j Quantification of i. k Loss of CEP44 leads to misalignment of mitotic spindles (>65%) generating either bipolar asymmetric spindles (51.3 ± 4.7%) or mono-/multipolar ones (14.3 ± 4.0). l Quantification of k. (a, b, d, h, i, k, scale bars: 10 μm, magnification scale bars: 1 μm; c, e, f, g, j and l data are presented as mean ± s.d., all statistics were derived from two-tail unpaired t-test analysis of n = 6 biologically independent experiments and source data are provided as a Source Data file).