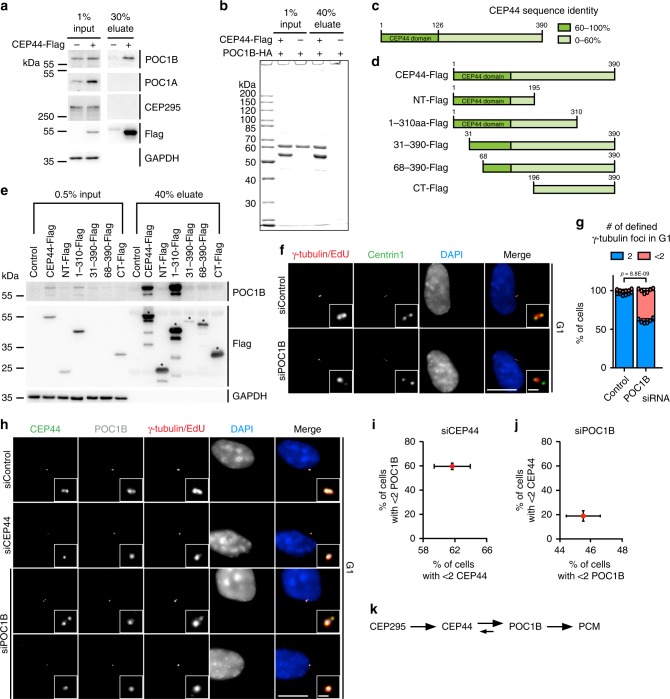
Fig. 3. The CEP44-POC1B complex is needed to convert centrioles to centrosomes.
a Anti-Flag IP using CEP44-Flag from RPE1 cells was analysed for POC1B, POC1A and CEP295 by immuno-blotting (IB). GAPDH was used as input control. b Coomassie Blue stained gel of in vitro binding between purified, recombinant CEP44-Flag and purified, recombinant POC1B-HA. See Supplementary Fig. 5b for IB and 5c for Coomassie Blue stained gels of purified proteins used in the experiment. c Schematic representation of CEP44 protein sequence identity in vertebrata (referred to Supplementary Fig. 5a). d CEP44-Flag constructs that were designed based on c and used in e. e IB of input and eluted samples from RPE1 IPs using CEP44-Flag constructs as outlined in d. The CEP44-Flag IPs were tested for the presence of POC1B. GAPDH was used as loading control for the input. f, g 39.2 ± 2.8% of G1 cells in which POC1B was depleted show <2 γ-tubulin defined foci (Cenp-F in Supplementary Fig. 5g). h–j Loss of either CEP44 or POC1B in response to siRNAs depletion by one of them. h, i CEP44 loss upon CEP44 siRNA has a similar impact on POC1B loss from dCs. i Quantification of h. h, j CEP44 delocalisation was less severe than POC1B loss upon POC1B siRNA. j Quantification of h. Upon siPOC1B depletion, CEP44 delocalised (18.9 ± 4.3% of G1 cells) less sever than POC1B (45.5 ± 2.3%). k Schematic representation of the functional interdependency between the conversion molecules in the CCC mechanism. (f, h, scale bars: 10 μm, magnification scale bars: 1 μm; g, i, j data are presented as mean ± s.d., all statistics were derived from two-tail unpaired t-test analysis of n = 6 biologically independent experiments and source data are provided as a Source Data file).