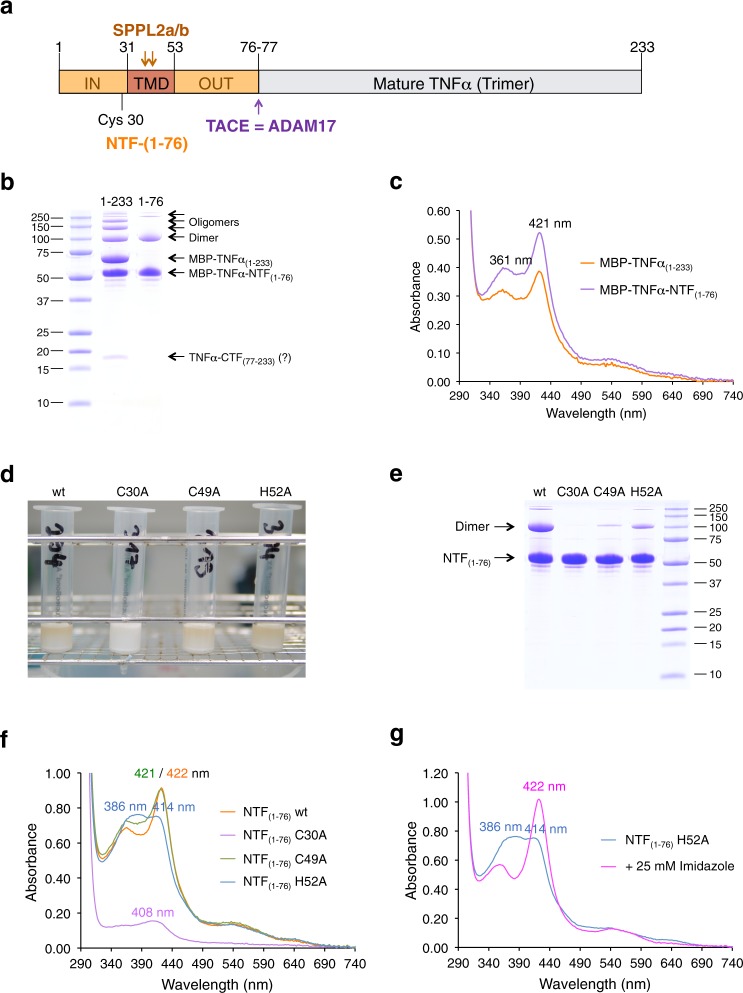
Fig. 2. TNFα is a heme-binding protein.
a Domain structure and proteolytical processing of TNFα 7. b Purification of full-length MBP-TNFα(1–233) and MBP-TNFα-ΝΤF(1–76) was followed by SDS-PAGE. MBP-TNFα(1–233) was partially degraded to a protein with the same size as MBP-TNFα-NTF(1–76) and a (copurified) 17 kDa protein (present as double band) which was most likely mature TNFα. c UV/VIS spectroscopy of purified MBP-TNFα(1–233) (orange trace) and MBP-TNFα(1–76) (violet trace). d Amylose chromatography of wt and mutant (C30A, C49A and H52A, respectively) MBP-TNFα-NTF(1–76). Amylose-affinity columns are shown after loading the columns with Triton X-100 solubilized membrane proteins and subsequent washing. e Purification of wt and mutant MBP-TNFα-NTF(1–76) proteins was followed by SDS-PAGE. f UV/VIS spectroscopy of wt and mutant (C30A, C49A, and H52A, respectively) MBP-TNFα-NTF(1–76) proteins; absorbance maxima are indicated. g To confirm that also MBP-TNFα-NTF(1–76) H52A bound heme, 25 mM imidazole was added to generate a Soret band at 422 nm. All proteins (apart from MBP-TNFα-NTF(1–76) C30A, which was purified only once) shown were purified at least twice and representative UV/Vis spectra are shown. Gel filtration of MBP-TNFα-NTF(1–76) wt and mutant H52A protein was done twice with the same outcome (see Supplementary Fig. 4).