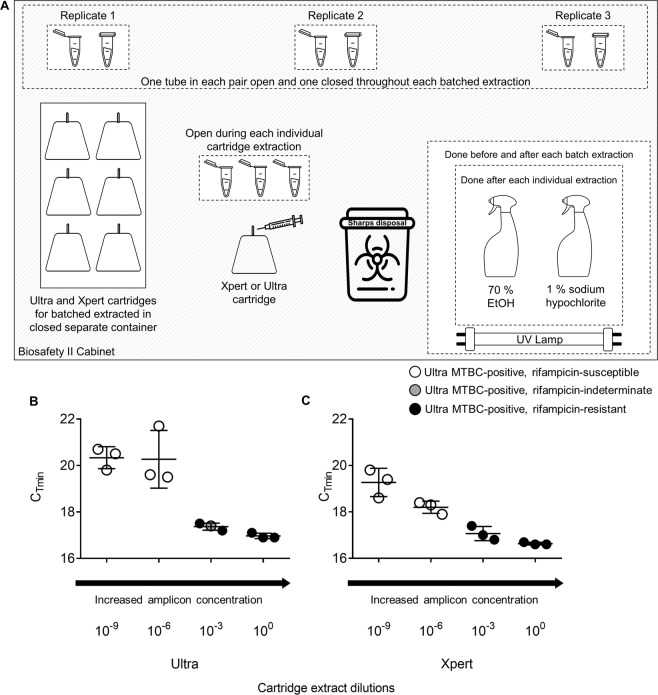
Figure 3.
Evaluation of rpoB cross contamination risk experimental set-up and results. (A) Configuration of the environmental exposure experiment within a Biosafety level 2 cabinet. Three microcentrifuge tubes were open throughout each batched extraction procedure and three remained closed [median (IQR) extractions per batch 17.5 (10.5–27.5)]. No exposed tubes were FT rpoB-positive. In parallel to evaluate if, in an absolute worst case scenario, rpoB cross-contamination was probable, dCE from a (B) Ultra or (C) Xpert done on a drug-resistant strain was added to a drug-susceptible strain and the resultant mixture tested by Ultra. When samples of DS-TB contained CE at higher concentrations (undiluted, 10−3), false-resistant (solid black circles) or indeterminate rifampicin resistance (grey circles) are seen. All samples containing CE dilutions beyond 10−6 showed true rifampicin susceptibility (white circles). Error bars represent CTmin values for each dilution. Some images were obtained from the Noun Project: microcentrifuge tube (without changes), Anthony Ledoux, https://thenounproject.com/term/eppendorf/1699532/; spray bottle (without changes), John Winowiecki, https://thenounproject.com/search/?q=spray%20bottle&i=2236898; sharps container, Juicy Fish (with changes), https://thenounproject.com/term/hospital-waste-bin/2450390/; needle (without changes), Creative Mania; https://thenounproject.com/search/?q=injection&creator=2251916&i=2409865.