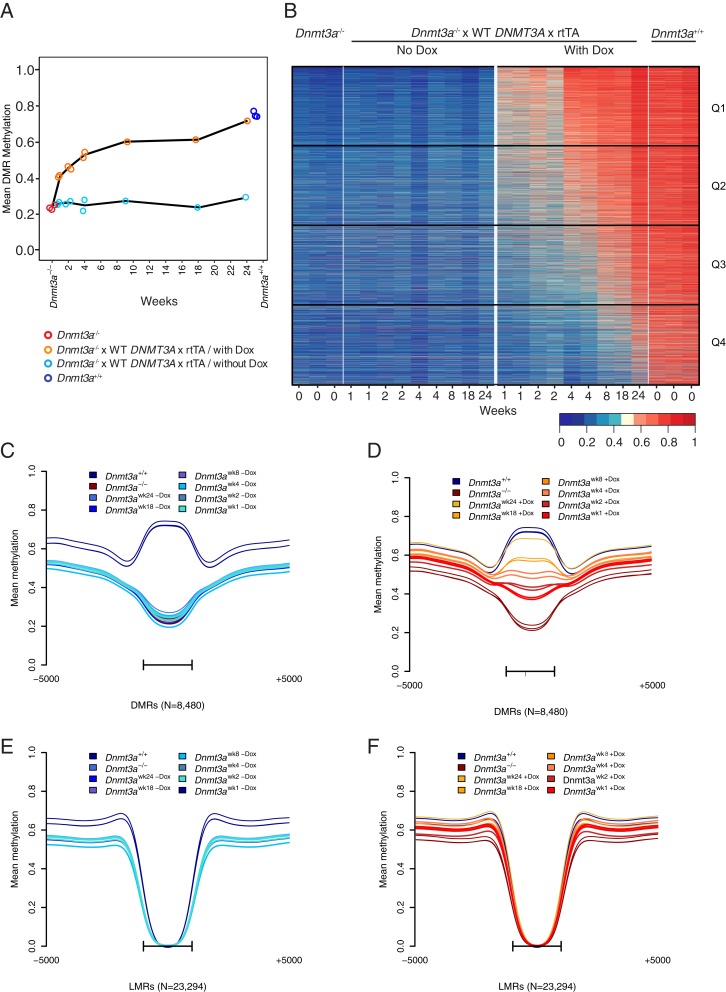
Fig. 3.
Restoration of DNMT3A expression is associated with remethylation of Dnmt3a−/−-dependent DMRs in bone marrow cells. (A) Global mean methylation of the 8,480 DMRs over time (weeks). Red dots represent Dnmt3a−/− as baseline values, followed by values for samples from mice fed with Dox (i.e., DNMT3A reexpression) for the designated time in weeks. There are two independent datasets for weeks 1, 2, and 4, and one dataset each for weeks 8, 18, and 24. By week 24, DNMT3A reexpression causes near-complete remethylation of these DMRs compared to the methylation levels in Dnmt3a+/+ bone marrow (dark blue dots). (B) Heatmap of mean methylation values from the 8,480 DMRs. The columns are grouped by Dnmt3a−/−, Dnmt3a−/− x WT DNMT3A x rtTA without and with Dox, and Dnmt3a+/+. Low methylation levels in the DMRs from marrow derived from the Dnmt3a−/− x WT DNMT3A x rtTA mice without Dox remain unchanged over time. Time-dependent restoration of methylation across all DMRs is observed in Dnmt3a−/− x WT DNMT3A x rtTA/with Dox, where the 24-wk time point shows near-WT levels of methylation. Quartiles of 2,120 DMRs representing fast (Q1), intermediate (Q2 and Q3), and slow (Q4) remethylating regions are shown on the right. (C and D) Aggregate (mean) methylation at 8,480 DMRs from Dnmt3a+/+ and Dnmt3a−/− samples (n = 3, each). DMRs from Dnmt3a−/− x WT DNMT3A x rtTA bone marrow (C) without Dox and (D) with Dox were plotted passively for the same 8,480 DMRs. In both C and D, DMRs have been scaled to a uniform length, and are shown with the adjacent 5 kb of flanking sequence. Bars represent the span of the scaled DMR regions. (E and F) Aggregate (mean) methylation at 23,294 LMRs. Dnmt3a−/− x WT DNMT3A x rtTA (E) without Dox and (F) with Dox were plotted passively for the same LMRs. In both E and F, LMRs have been scaled to a uniform length and are shown with the adjacent 5 kb of flanking sequence. Bars represent the span of the scaled LMR regions.