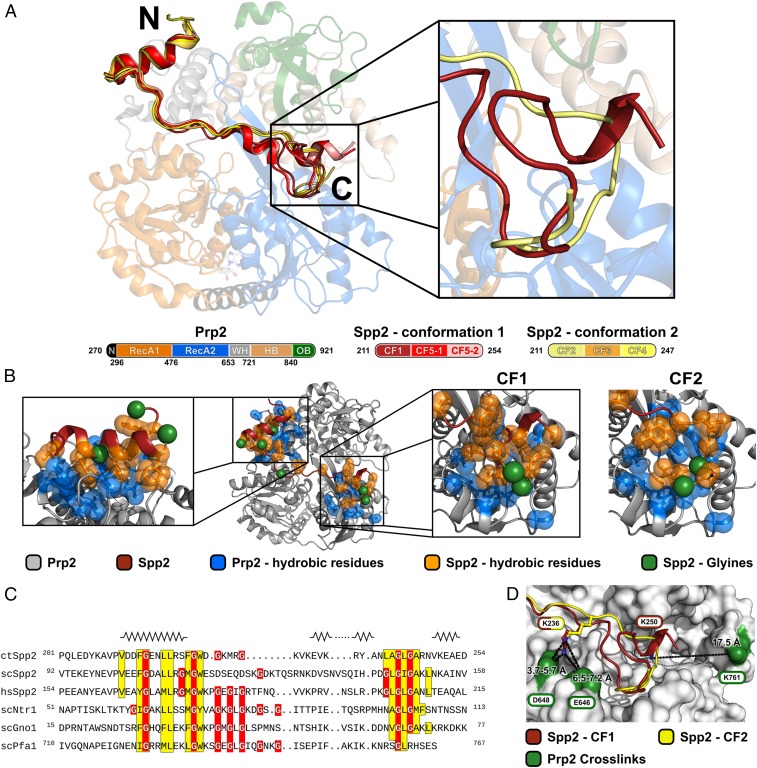
Fig. 2.
Structural overview of the ctSpp2 G-patch bound to ctPrp2. (A) The model of the ctPrp2-ctSpp2211–254 complex depicted as a cartoon model, with ctPrp2 displayed semitransparently. N-terminal residues (270 to 296) of ctPrp2 are shown in black, the RecA1 domain (297 to 476) is shown in orange, the RecA2 domain (477 to 653) is shown in blue, the WH domain (654 to 721) is shown in gray, the HB domain (722 to 840) is shown in wheat, and the OB domain (841 to 921) is shown in green. Two alternative conformations of the ctSpp2 G-patch were found in complex structures obtained from five crystal forms (CFs). ctSpp2211–254 molecules exhibiting conformation 1 are depicted in different shades of red, whereas molecules belonging to conformation 2 are displayed in different shades of yellow. (Right) A zoomed-in view of the alternative conformations at the C-terminal end of the G-patch with one representative for each conformation. (B) Overview of hydrophobic interactions between ctSpp2211–254 and ctPrp2. Hydrophobic residues of ctSpp2 are shown in orange, while hydrophobic residues of ctPrp2 within 8 Å of the conserved ctSpp2211–254 hydrophobic residues are displayed in blue. Glycine residues of ctSpp2211–254 are highlighted as green spheres. (C) Sequence alignment of the G-patch domains of Spp2 from C. thermophilum, S. cerevisiae, and H. sapiens together with Ntr1, Gno1, and Pfa1 from S. cerevisiae. Conserved hydrophobic residues are highlighted in yellow, and glycine residues are shown in red. Secondary structure elements present in any of the five crystal forms are displayed on top of the corresponding segment of the sequence. The N-terminal amphipathic helix, as well as a hydrophobic stretch at the C-terminal end, are highly conserved. (D) Residues identified to cross-link to the lysines K236 and K250 of ctSpp2211–254 are shown as sticks and the cross-linked residues on ctPrp2 are shown in green.