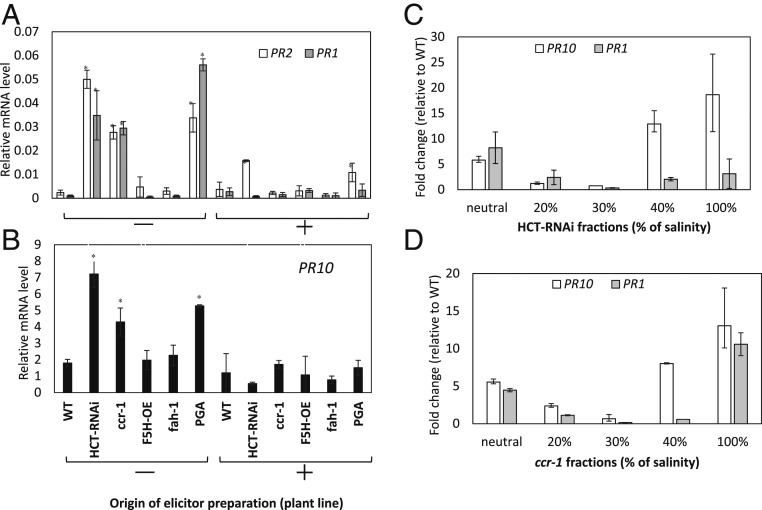
Fig. 2.
Defense gene expression in Arabidopsis cell cultures in response to water-soluble elicitors from cell walls of wild-type (WT), HCT-RNAi, ccr1, and f5h (fah-1) mutant and F5H overexpressor (OE) Arabidopsis plants. (A) PR1 and PR2 induction in response to crude elicitors from the plant lines shown. (B) PR10 induction in response to crude elicitors from the plant lines shown. (C) PR10 and PR1 induction by ion exchange fractionated elicitors from cell walls of HCT-RNAi plants. (D) PR10 and PR1 induction by ion exchange fractionated elicitors from cell walls of ccr1 plants. The elicitor activity of selected fractions was determined by measuring their ability to induce defense gene transcripts (PR2, PR10, PR1) in cell suspension cultures. Analysis of transcript levels in cell cultures was by qRT-PCR performed with total messenger RNA (mRNA) from suspension cells harvested 12 h postelicitation, and incubated in the dark at 25 °C. Transcript levels are expressed relative to AtPP2A. Results are means ± SD of three biological replicates. Asterisks in A and B indicate significant differences from WT (P < 0.05) by pairwise multiple comparison Tukey test. Elicitor extracts were prepared from the AIR fraction of cell walls. Extracts were added directly to cell cultures (−), or pretreated with PGase (+). PGA was also tested as elicitor for a positive control. Elicitor fractions are as shown in SI Appendix, Fig. S7 A–D.