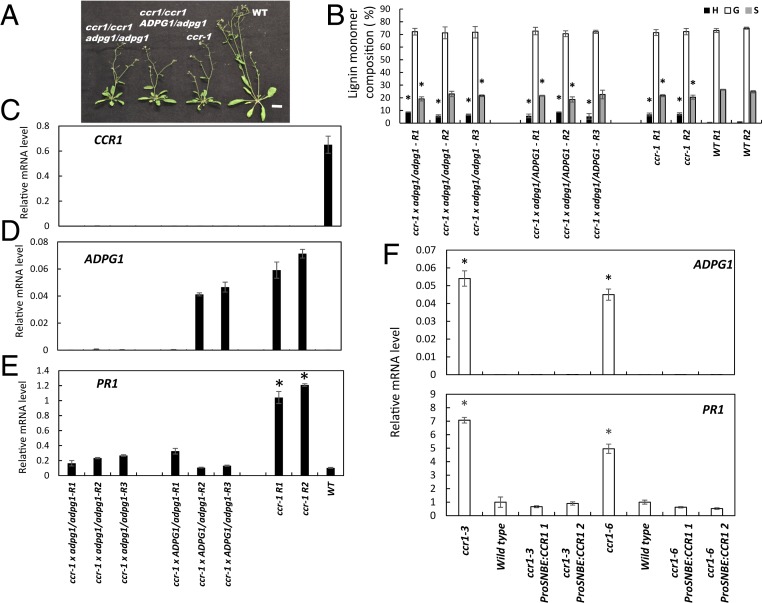
Fig. 4.
ADPG1 is required for PR1 induction in the ccr1 mutant of Arabidopsis. (A) Phenotype of F2 progeny of the cross ccr1 x adpg1. Wild-type (WT), ccr1, and F2 plants are 7 wk old. (Scale bar, 2 cm.) (B) Lignin content and composition of F2 progeny of the cross ccr1 x adpg1 as determined by thioacidolysis. Results are means ± SD of five technical replicates. Individual biological replicates are indicated by R1, R2, etc. (C) Levels of CCR1 transcripts in WT and ccr1/adpg1 mutant lines. (D) Levels of ADPG1 transcripts in WT and ccr1/adpg1 mutant lines. (E) Levels of PR1 transcripts in WT and ccr1/adpg1 mutant lines. Genotypes are represented as uppercase (WT) and lowercase (mutant) alleles. Transcript analyses were performed on 8-wk-old plants, and expressed relative to ACT2. In C–E, each replicate is a pool of four plants of the same genotype. (F) Restoring CCR expression to xylem prevents ADPG1-mediated induction of PR proteins in the Arabidopsis ccr1 mutant. PR1 transcript levels were determined in inflorescence stems of ccr1 mutant plants (two independent lines, ccr1-3 and ccr1-6), and the ccr1 mutants in which a WT copy of CCR1 was expressed under a xylem-specific promoter (ProSNBE:CCR1) (see ref. 40 for details of the lines). Results are mean ± SD of three biological replicates; WT PR1 transcript value is normalized to 1.0. Asterisks in B, E, and F indicate significant differences from WT (P < 0.05) by pairwise multiple comparison Tukey test.