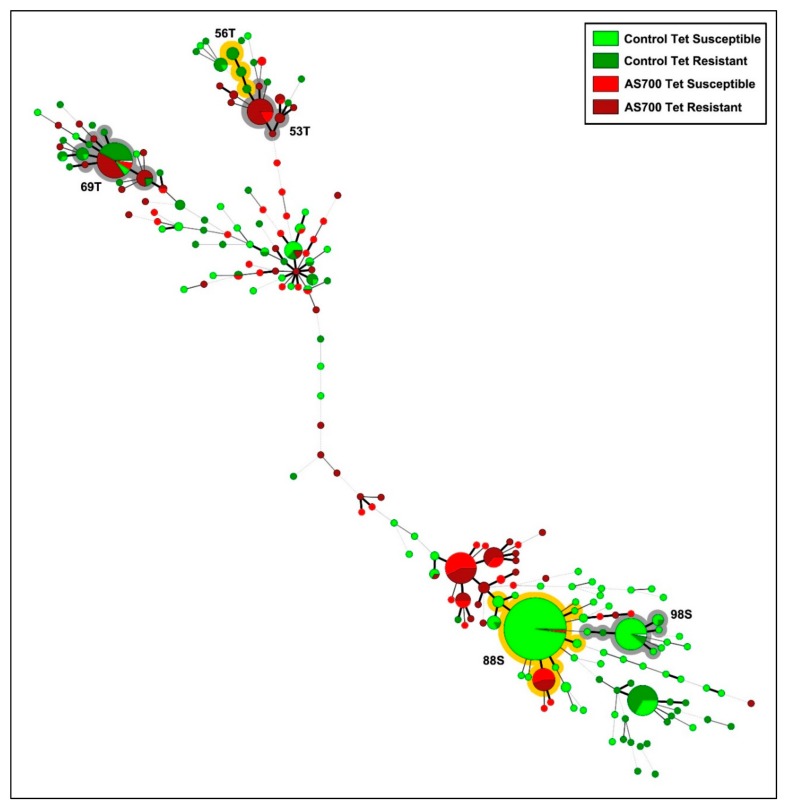
Figure 6.
Campylobacter jejuni comparative genomic fingerprinting (CGF) subtypes recovered from beef cattle throughout the production continuum that were administered chlortetracycline and sulfamethazine (i.e., AS700 treatment) or no antibiotics (i.e., control treatment), and were resistant or susceptible to tetracycline. The minimum spanning tree was generated in Bionumerics (version 6.6, Applied Maths), and data were combined across pens and sample type. The size of the circle is proportional to the number of isolates within each CGF subtype (100% level of resolution), the thickness of lines connecting subtypes represent mismatched loci (i.e., one to three loci), and subtypes with no line represent ≥ four mismatched loci between respective subtypes. Shading illustrates subtype clusters that were predominantly tetracycline resistant (T) or tetracycline susceptible (S). Numbers associated with clusters indicate subtype cluster identifiers.