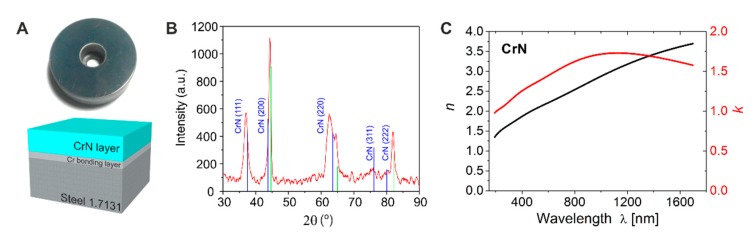
Figure 1.
(A) Picture of the actual sample with a sketch that illustrates the steel 1.7131 substrate, covered with a 200 nm Cr film for bonding a 2.5 µm thick chromium nitride (CrN) top layer. (B) X-ray diffraction (XRD) data of a non-irradiated area of a CrN samples as displayed in (A), including peaks corresponding to iron (marked green) and a CrN form known as Carlsbergite (marked blue). (C) Plot of the refractive index n (left axis) and the extinction coefficient k (right axis) of the CrN layer for different wavelengths as measured by ellipsometry. In our calculations we used n = 2.439 and k = 1.623 for λ = 800 nm.