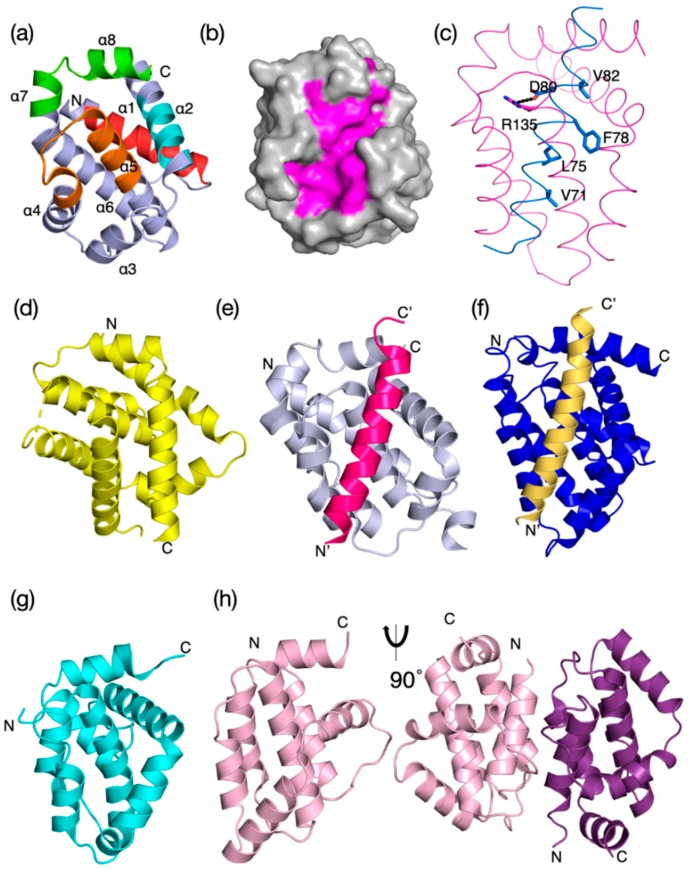
Figure 3.
Evolutionary structure conservation in the Bcl-2 family and their complexes. Ribbon representation of the 3D structures of prosurvival and proapoptotic Bcl-2 family members and their complexes are shown. The helical bundle Bcl-2 structure occurred early in evolution and changed little over evolutionary time scales. (a) H. sapiens Bcl-xL (PDB 1R2D) with BH1–4 motifs colored in orange, green, cyan, and red as shown in the sequence–structure alignment of Figure 2a, (b) H. sapiens Bcl–xL (PDB 1R2D) shown as grey surface with canonical ligand-binding groove shaded in magenta, (c) BHP2 from the sponge G. cydonium Bcl-2, BHP2 (PDB 5TWA) magenta, LB–Bak sky blue. The canonical ionic interaction between the conserved Arg from prosurvival Bcl-2 and conserved Asp from the BH3 motif of prodeath Bcl-2 as well as the four conserved hydrophobic residues from the Bak BH3 motif are shown as sticks. (d) M. musculus Bax (PDB 5W62) yellow, (e) H. sapiens Bcl-b:Bim complex (PDB 4B4S), (f) C. elegans CED-9: EGL-1 complex, CED-9 (navy) with EGL–1 (sand) in the binding groove (PDB 1TY4). (g) Myxoma virus Bcl-2 M11L (PDB 2JBX) cyan, (h) Vaccinia virus N1L (PDB 2I39) salmon. Monomeric N1 is shown in the same orientation as in (a), and the functionally relevant dimer is shown rotated by 90o around the vertical axis. In (a), the extent of the BH motifs is indicated as ribbon colored as in Figure 2a and the helices α1–α8 are also indicated. The structures were aligned on human Bcl-xL and the orientation for all structures is the same as that in (a). The N and C termini are indicated.