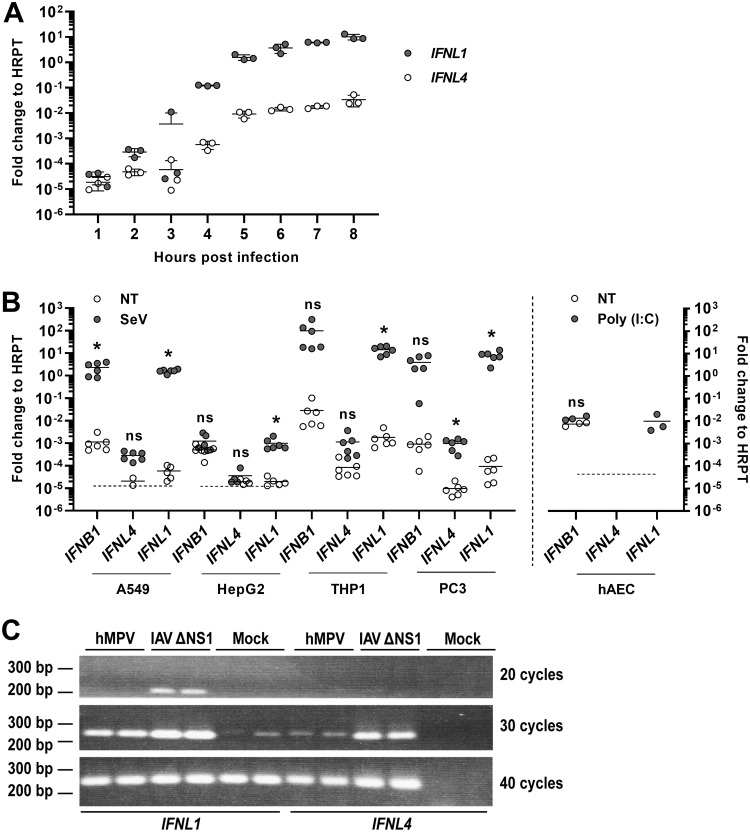
FIG 1.
Expression of the IFNL4 gene is not virus inducible. (A) A549 (an adenocarcinomic alveolar basal epithelial cell line) cells were infected with SeV, and the expression levels of IFNL4 and IFNL1 genes were quantified by reverse transcription quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR) at the indicated time points. Data were calculated relative to internal expression of HPRT. The experiment was performed in biological triplicates, and data are presented as a scatter plot with mean ± standard deviation (SD) (n = 3). (B) A549, HepG2 (a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line), macrophage-like differentiated THP-1 (a monocyte-like cell line before differentiation), and PC-3 (a prostate cancer cell line) cells were mock infected or infected with SeV for 6 h, whereas human airway epithelial cell (hAEC) cultures were mock treated or treated with poly(I·C) for 18 h. Expression levels of IFNB1, IFNL4, and IFNL1 genes were quantified by RT-qPCR. Data were calculated relative to internal expression of HPRT. The dashed line indicates the detection limit in those cases where mRNA levels could not be determined for some replicates because they were too low. The experiment was performed in biological sextuplicates (left panel) or triplicates (right panel), and data are presented as a scatter plot with mean ± SD (n = 3 or 6). Statistical significance was determined using an unpaired t test. *, 0.01 < P < 0.05; ns, P ≥ 0.05. (C) A549 cells were mock infected or infected with human metapneumovirus (hMPV) or influenza A virus (IAV) ΔNS1 for 18 h. Expression levels of IFNL1 and IFNL4 mRNA were assessed by semiquantitative PCR and vizualised by agarose gel electrophoresis. The experiment was performed in biological duplicates.