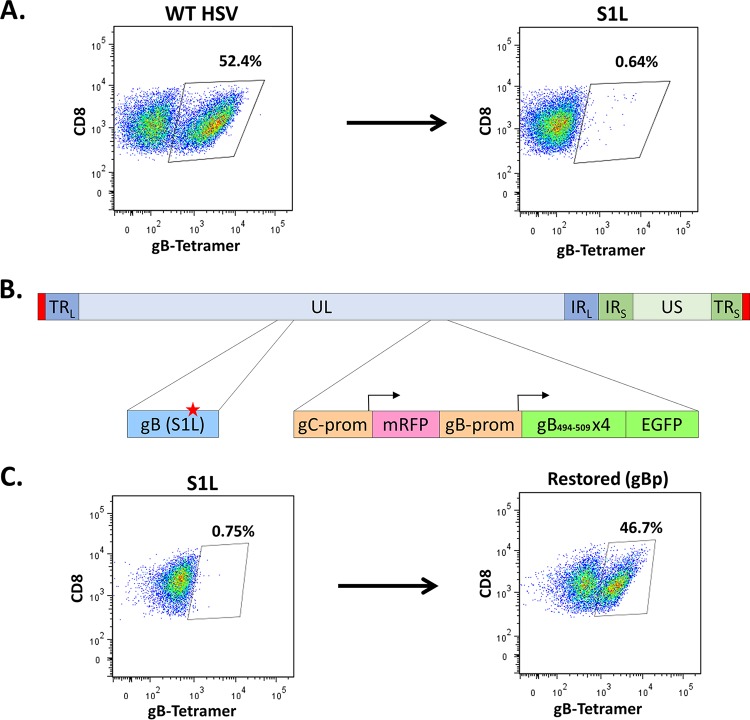
FIG 1.
Ectopic restoration of an immunodominant gB498–505-specific CD8+ T cell response. B6 mice were infected at 1 × 105 PFU/eye with either WT KOS strain, S1L, or the ectopically restored gBp virus. At 8 days postinfection, TG single-cell suspensions were stained with anti-CD45, anti-CD3, anti-CD8, and gB498–505 tetramer. Depiction is gated to show only CD8 staining cells and gB498–505 tetramer staining, and the fraction is the gB tetramer-stained cells as a fraction of the total ganglionic CD45+ CD3+ CD8+ T cells. These data are representative of one experiment that was repeated at least 3 times (n = 5 mice/group). (A) Representative flow cytometry demonstrating MHC-I gB498–505 tetramer staining of total ganglionic CD8+ T cells in mice infected with WT HSV or HSV with the S1L epitope point mutation in gB. (B) Depiction of ectopically restored gB peptide expressing virus. In a gB-S1L point mutation parental strain, the native gC promoter drives a monomeric red fluorescent protein (mRFP) transcriptionally terminated by a BGH signal, followed by an inserted gB promoter driving (gB494–509)4 linked in frame to EGFP. (C) Representative flow cytometry of gB498–505 tetramer staining of total ganglionic CD8+ T cells in mice infected with HSV S1L or HSV expressing gB498–505 epitope containing multimers linked to EGFP under the control of the gBp. TRL, terminal repeat long; UL, unique long region; IRL, inverted repeat long; IRS, inverted repeat short; TRS, terminal repeat short; prom, promoter.