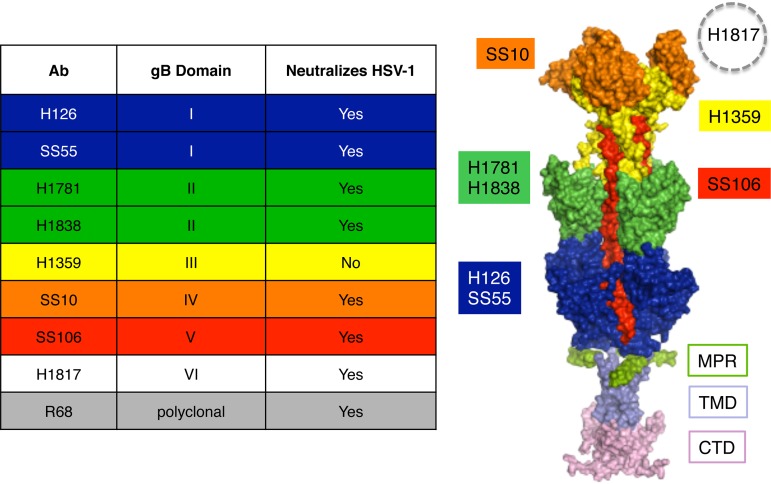
FIG 1.
Antibodies to HSV-1 gB and their epitopes. (Left) List of gB antibodies used in this study, the gB domains to which they bind, and HSV neutralization activities. The ectodomain, membrane-proximal region (MPR), transmembrane domain (TMD), and cytoplasmic tail domain (CTD) of the postfusion form of the gB trimer are shown (37). Monoclonal antibody-resistant mutations in domain I, which contains bipartite hydrophobic fusion loops, map to amino acid residue 303 for H126 and residues 203, 335, and 199 for SS55 (38, 39). MAbs H1781 and H1838 bind to domain II and map to residues 454 to 473 and 391 to 410, respectively (13). MAb H1359 binds to domain III and maps approximately to residues 487 to 505 (30). MAb SS10 binds to domain IV and maps to residues 640 to 670 (13). MAb SS106 binds to domain V and maps to a peptide spanning residues 697 to 725 (29). MAb H1817 binds to domain VI (not resolved in the structure) and maps to residues 31 to 43 (13).