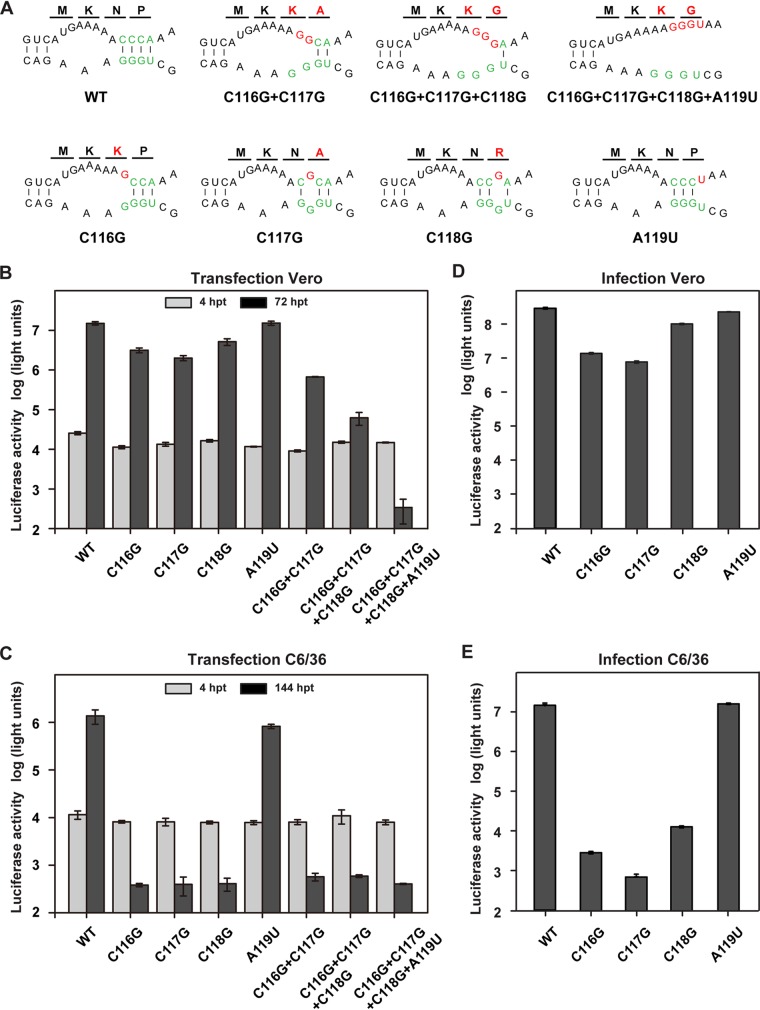
FIG 3.
Functional analysis of complementarity between DAR elements using the Rluc-ZIKV-T154C reporter virus. (A) Mutations introduced into theDAR sequences within the C38 region of Rluc-ZIKV-T154C. Predicted interaction between 5ʹ and 3ʹ DAR elements and their adjacent regions. The DAR sequences are labeled in green, and the mutations targeting the 5ʹ DAR are highlighted in red. The first four amino acids of the capsid encoded by each mutant RNA are shown above the nucleotide sequences, and the mutated amino acids are in red. (B and C) Translation and replication of the Rluc-ZIKV mutants in Vero (B) and C6/36 (C) cells. Equal amounts of WT and mutant RNAs were transfected into Vero or C6/36 cells, and the luciferase activity was measured at 4 hpt and 72 hpt in Vero cells and at 4 hpt and 144 hpt in C6/36 cells. (D and E) Infectivity of mutant reporter viruses in Vero (D) and C6/36 (E) cells. Viruses harvested from mutant-RNA-transfected Vero cells at 72 hpt were used to infect naive Vero and C6/36 cells at the same MOI of 0.1, and the luciferase activity was detected at 72 hpi in Vero cells and at 112 hpi in C6/36 cells. The data are representative of three independent experiments. Each experiment was performed in triplicate, and the error bars represent standard deviations.