Figure 3.
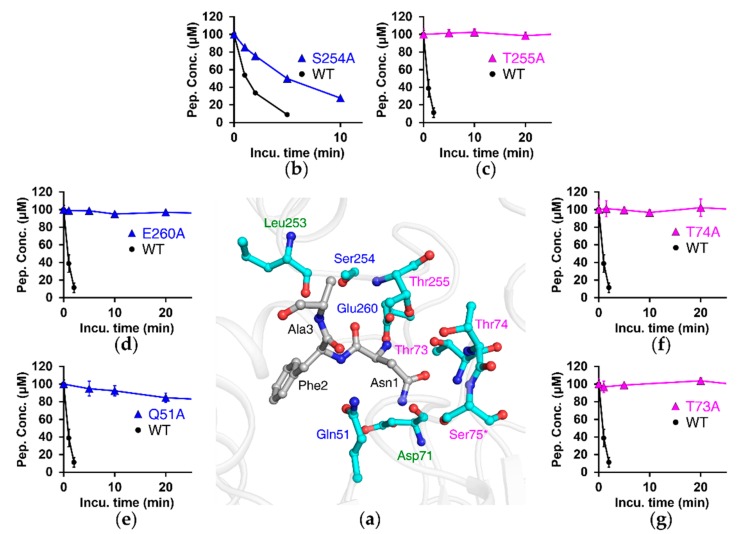
Residues interacting with substrate peptide through hydrogen bonds or salt bridges are crucial in catalytic activity of NTAN1. (a) Structure of NTAN1 C75S mutant in complex with the NFAAR pentapeptide at the active site. NTAN1 residues interacting with the peptide through hydrogen bonds or salt bridges are shown in cyan ball-and-stick model (Ser75 mutated from catalytic Cys75 is labeled with an asterisk). Thr73, Thr74, and Thr255 interact with the peptide via both their side chains and backbones, and are labeled in magenta. Gln51, Ser254, and Glu260 interact with the peptide via only side chains, and are labeled in blue. Asp71 and Leu253 interact with the peptide via only backbones, and are labeled in green. The bound peptide is colored in gray. Nitrogen and oxygen atoms are colored in blue and red, respectively. (b–g) Deamidation activities by Ala-mutants of NTAN1 residues described in (a). Concentrations of the NRAAA peptide are plotted against incubation times with NTAN1 WT and mutants, S254A (b), T255A (c), E260A (d), Q51A (e), T74A (f), and T73A (g). Error bars indicate standard-deviation values of three independent experiments.