Table 5.
Summary of the results for various piperine (Pip) delivery methods.
| Piperine Delivery Method | Structure | Solubility and Release Kinetics | Targeting Specifications |
|---|---|---|---|
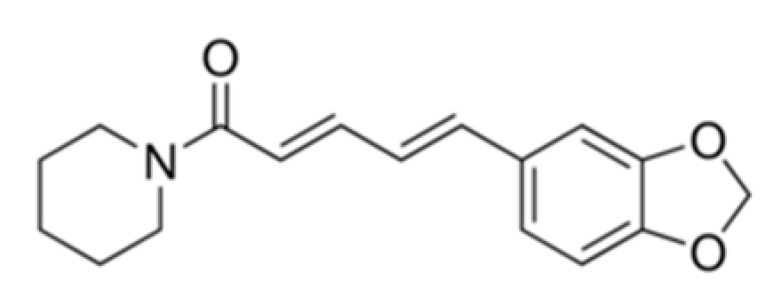
| Pip (free form) |
|
Higher solubility in PBS at acidic pH 5 than 6.8, 7.4, and 9. | Moderate cytotoxicity towards normal WI-38 cells. Weak activity against HCT116 colon cancer cells (monolayer and spheroids). Not effective. Non-targeting for colon. |
| HAP-Pip or HAP-P-Pip—Pip-loaded HAP not modified or modified with phosphonate. Loading at pH 7.2 and 9.3 |
|
Short-term release. Release 100% of Pip capacity ~36 h (pH 6.8) and 24 h (pH 5). | Moderate cytotoxicity towards normal cells. High anticancer effect on monolayer colon cancer cells but not spheroids. Not enough cancer targeting. No change in cell morphology in monolayer or spheroids. |
| HAP-P-Pip9.3-GA-FA—Pip-loaded HAP modified with phosphonate, coated with gum Arabic, and conjugated to folic acid |

|
Long-term release. Release 100% of Pip capacity ~84 h (pH 6.8) and 72 h (pH 5). | Less cytotoxicity. High anticancer effect with full inhibition of monolayer HCT116 cells and ~60% inhibition for spheroids. High cancer-targeting of monolayer and spheroid HCT116 cells. Cancer targeting through folate receptors. Cell morphology changes: smaller size, shrinkage, and defragmentation of spheroids. |
