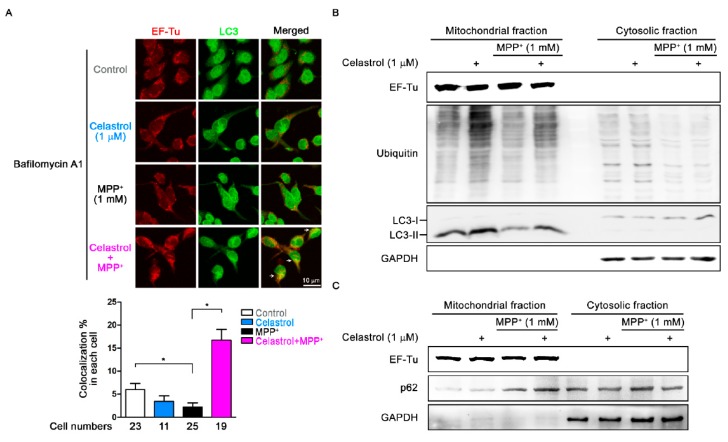
Figure 5.
Celastrol enhances the clearance of damaged mitochondria via activating mitophagy. This study used 1 mM MPP+ to induce mitochondrial dysfunction and 100 nM bafilomycin A1 pretreatment for 30 min to inhibit autophagosomes fusion with lysosomes in SH-SY5Y cells. (A) Images of immunodouble staining obtained from confocal microscopy show that MPP+ but not celastrol treatment reduced dysfunctional mitochondria co-localized with autophagosomes as compared to control. In the celastrol + MPP+ group, celastrol enhanced MPP+-induced dysfunctional mitochondria co-localized with autophagosomes as compared to MPP+ alone. Here, we used anti-EF-Tu and anti-LC3 antibodies to stain mitochondria and autophagosomes, respectively. The colocalization of EF-Tu and LC3 was indicated by arrows. Summarized results of the percentage of colocalization in each cell are given as the mean ± SEM (n = 11–25). p-value was determined using the Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison post hoc test. * p < 0.05 as compared to control. (B) Western blot results of mitochondrial fractions and cytosolic fractions from cells show that celastrol but not MPP+ enhanced ubiquitinated and LC3-II bound mitochondria as compared to control in mitochondria fractions; celastrol cotreatment with MPP+ enhanced it as compared to MPP+ alone. (C) MPP+ but not celastrol treatment increased p62 conjugation in the mitochondrial fraction as compared to control; celastrol cotreatment with MPP+ enhanced it as compared to MPP+. Here, we used EF-Tu and GAPDH to identify the purity of mitochondrial and cytosolic fractions, respectively.