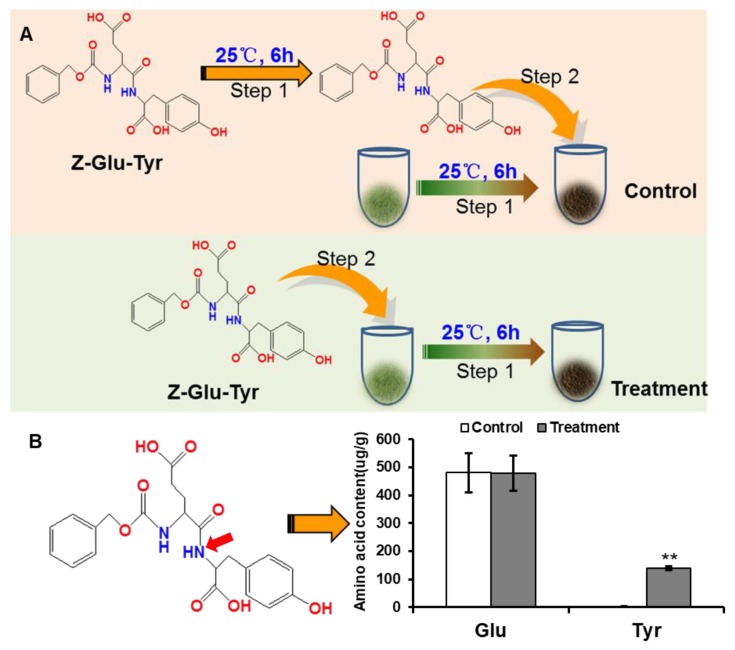
Figure 2.
Identification of protein degradation during black tea fermentation with an artificially synthesized dipeptide benzyloxycarbonyl glutamyl-tyrosin (Z-Glu-Tyr). (A) Schematic diagram of experimental design. Control: Z-Glu-Tyr and tea leaves powder were fermentation respectively at 25 °C for 6 h, and then mixed to detect the contents of free Glu and Tyr. Treatment: Z-Glu-Tyr and tea leaves powder were mixed first, and then companied fermentation at 25 °C for 6 h step 1, Z-Glu-Tyr and tea leaves powder were fermentation at 25 °C for 6 h respectively (control) or mixed (treatment); step 2, Z-Glu-Tyr mixed with tea leaves powder. (B) Changes of Glu and Tyr content after enzymatic reaction during the fermentation. Data shown as the mean ± SD (n = 3). ** p < 0.01 vs. Control.