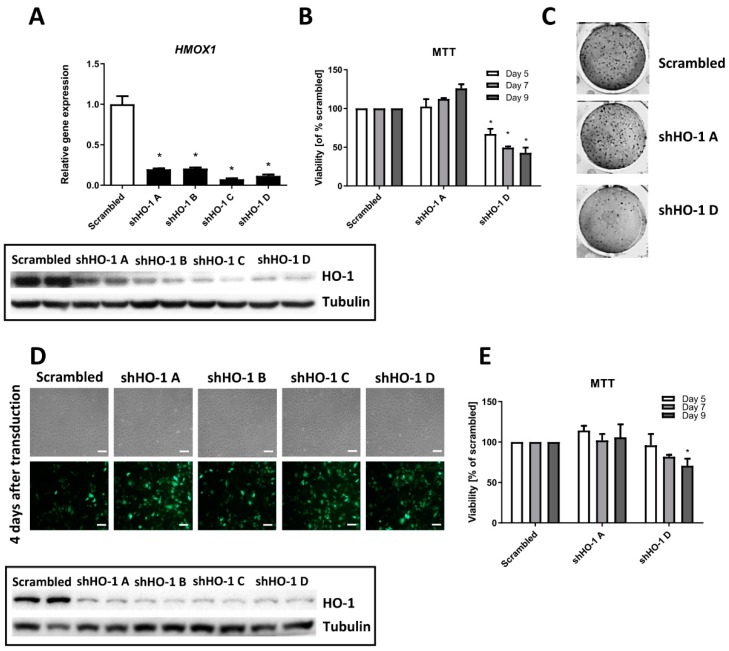
Figure 4.
Genetic inhibition of HMOX1 in the NCCFH1 and UOK 268 cell lines exert similar effects as in UOK 262 cells. FH-deficient cell lines were transduced with lentiviral vectors encoding four shRNA sequences against HMOX1 transcript and with one, non-specific scrambled shRNA. (A) qRT-PCR results of HMOX1 silencing level in NCCFH1 cell line after transduction with HO-1 shRNA sequences and scrambled shRNA presented as relative fold change (mean ± SD, upper panel); a representative picture of Western blot analysis of HO-1 after transduction (lower panel). (B) MTT viability assay on NCCFH1 cells after several time-points (5–9 days) from transduction, presented as the percentage of scrambled shRNA (mean ± SD). (C) Representative pictures of colony formation assay on the NCCFH1 cell line after 14 days after transduction with shHO-1. (D) Microscopic images of UOK268 cells both in the bright field (upper part) and under fluorescence (lower part) 4 days after transduction with lentiviral vectors encoding shHO-1 and scrambled; scale bar: 100 µm. (E) MTT viability assay on UOK268 cells after several time-points (5–9 days) from transduction, presented as the percentage of scrambled shRNA (mean ± SD). * p < 0.05 vs. scrambled sequence, Student’s t-test.