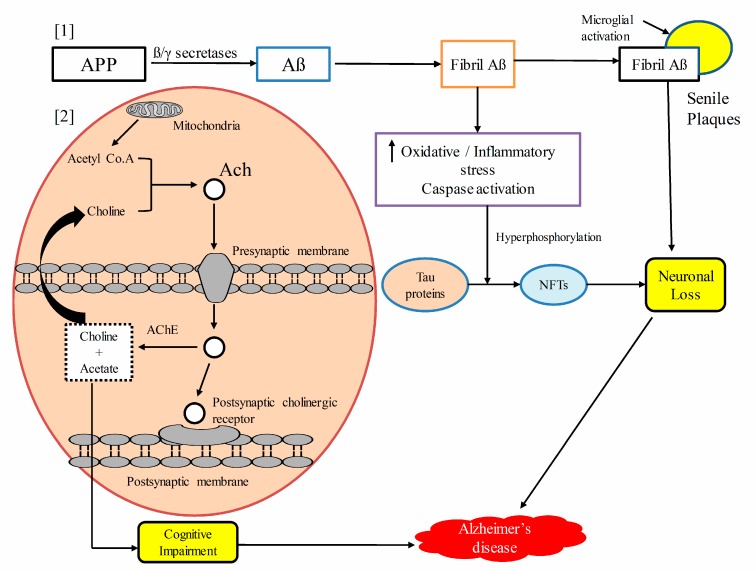
Figure 3.
Schematic presentation of the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. [1] Amyloid precursor protein (APP) is hydrolyzed by β and γ secretases to form β-amyloid (Aβ), which aggregates to form fibril Aβs. Fibril Aβs upregulate oxidative stress, the inflammatory cascade, and caspase activation, which results into the hyperphosphorylation of the Tau protein to form neurofibrillary tangles(NFTs), and the ultimate result is neuronal cells loss. Extensive fibrils along with activated microglia accumulated to form senile plaques, which lead to neuronal and synaptic loss. [2] Upstream regulating acetyl cholinesterase (AChE) enzyme promotes acetylcholine (Ach) degradation, resulting in neurotransmitter deficit, which leads to cognitive impairment. Amyloid precursor protein (APP), amyloid beta proteins (Aβ), neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs), acetylcholine (Ach), acetyl cholinesterase (AChE).