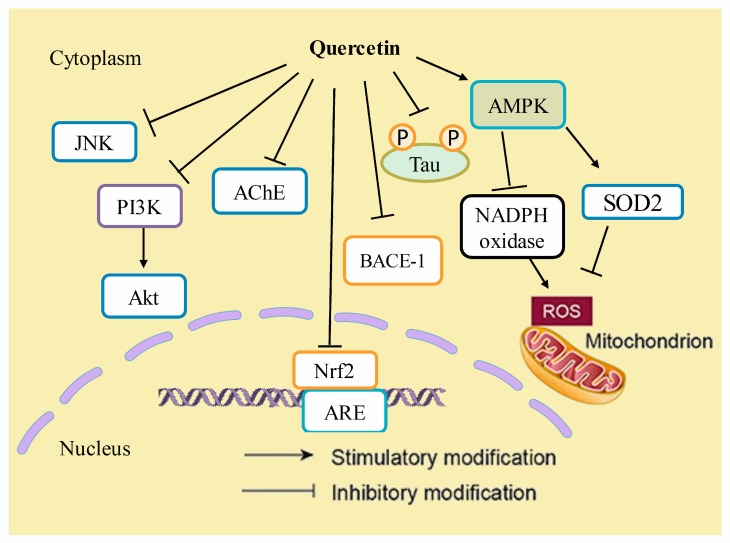
Figure 5.
Mechanistic insights of quercetin in Alzheimer’s disease. Quercetin has inhibitory effects on JNK, PI3K/Akt pathways, acetyl cholinesterase (AChE), nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf-2), beta-secretase-1 (BACE-1) enzyme activity, and the hyperphosphorylation of tau proteins. On the other hand, it stimulates the expression of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), which thereby decreases reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation by inhibiting NADPH oxidase activity or by increasing the antioxidant activity of enzymes such as superoxide dismutase-2 (SOD2).