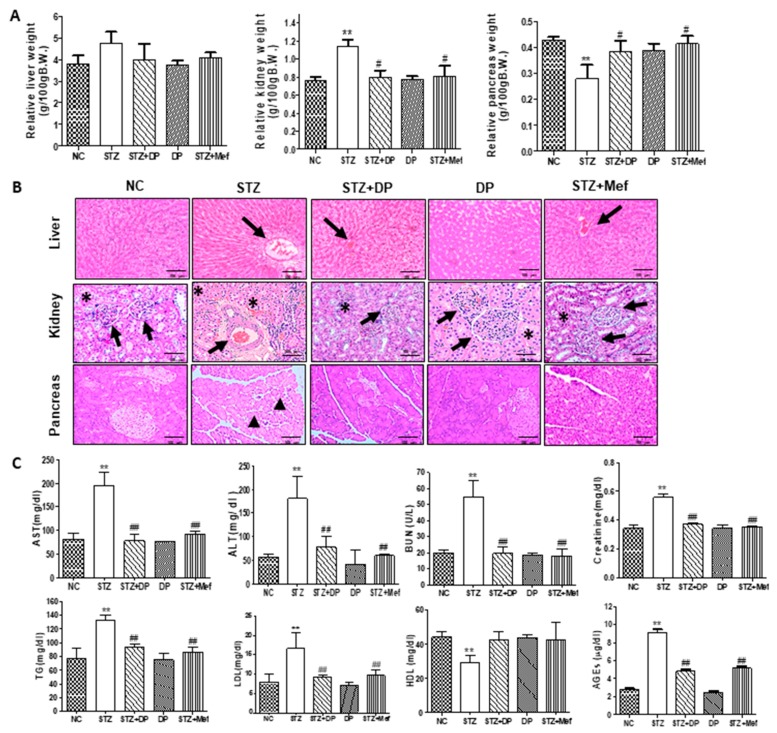
Figure 3.
Effect of DP extract on relative organ weight, histopathological changes, and biochemical parameters in STZ-induced diabetic rats. (A) Relative organ weight changes in STZ-induced diabetic rats. Values are expressed as the mean ± S.D. for six rats. Statistical analysis was performed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD post hoc test for multiple comparisons. ** p < 0.01 compared to vehicle control; # p < 0.05 compared to STZ-treated group. (B) Representative histology of hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stained liver, kidney, and pancreatic sections from experimental groups. STZ-induced rats showed enlarged cortex with glomerular sclerosis (arrowheads) and expansion (asterisk), and they also showed dilatation. The cortex from DP extract-treated rats displayed a normal histological structure of tubules and collecting ducts. The islet cells are seen interspersed between the acinar cells. The islets appeared more lightly stained than the surrounding acinar cells. STZ-induced diabetic rats revealed pathological changes in the acinar cells, which were observed as swollen and small vacuoles (black arrowheads). Islet β-cells are almost entirely lost in STZ-induced diabetic rats. However, the administration of DP extract showed distortion of the general architecture. An atrophic change of the acinar cells was less severe, and the border between exocrine and endocrine portions became more distinct. Images are representative of three animals per experimental group (magnification 100×). (C) Effect of DP extract on biochemical parameters. Values are expressed as the mean ± S.D. for six rats. Statistical analysis was performed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD post hoc test for multiple comparisons. ** p < 0.01 compared to vehicle control; ## p < 0.01 compared to the STZ-treated group.