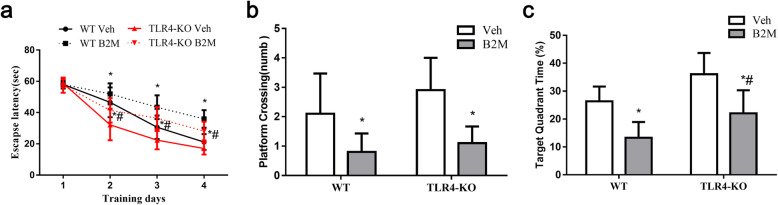
Fig. 1.
TLR4 elimination prevented cognitive dysfunction following B2M treatment. All groups of mice were trained in Morris water maze (MWM) test 23 days after B2M or vehicle treatment (n = 10/subgroup). TLR4 elimination attenuated spatial learning and memory dysfunction caused by B2M. The escape latency measured as mean time (a) were detected within 4 consecutive days. On the 28th day after treatment, the probe trail was conducted to record the platform crossing times (b) and mean percentage of time in the target quadrant (c). The data were analyzed using two-way ANOVAs used Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Values are presented as the means ± SD. Significant differences are expressed as follows: *p < 0.05 vs. Veh group, #p < 0.05 vs. B2M group for WT mice. MWM = Morris water maze, WT = wild type C57BL/6, TLR4-KO = TLR4 knockout