Fig. 2.
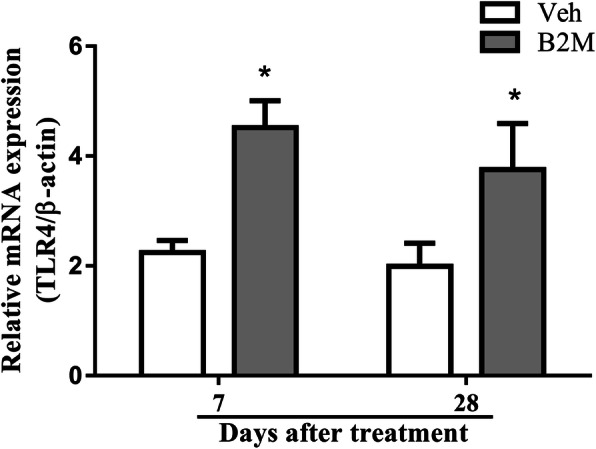
B2M-induced cognitive dysfunction was partially dependent on TLR4 activation. Expression of TLR4 mRNA in hippocampus of WT mice; β-actin was used as an endogenous reference gene. B2M induced a significantly higher expression of TLR4 mRNA in hippocampus (n = 6/subgroup). The data were analyzed using one-way ANOVAs with post-hoc pairwise comparisons. Values are presented as the means ± SD. Significant differences are expressed as follows: *p < 0.0001 vs. Veh group in WT mice. WT = wild type C57BL/6
