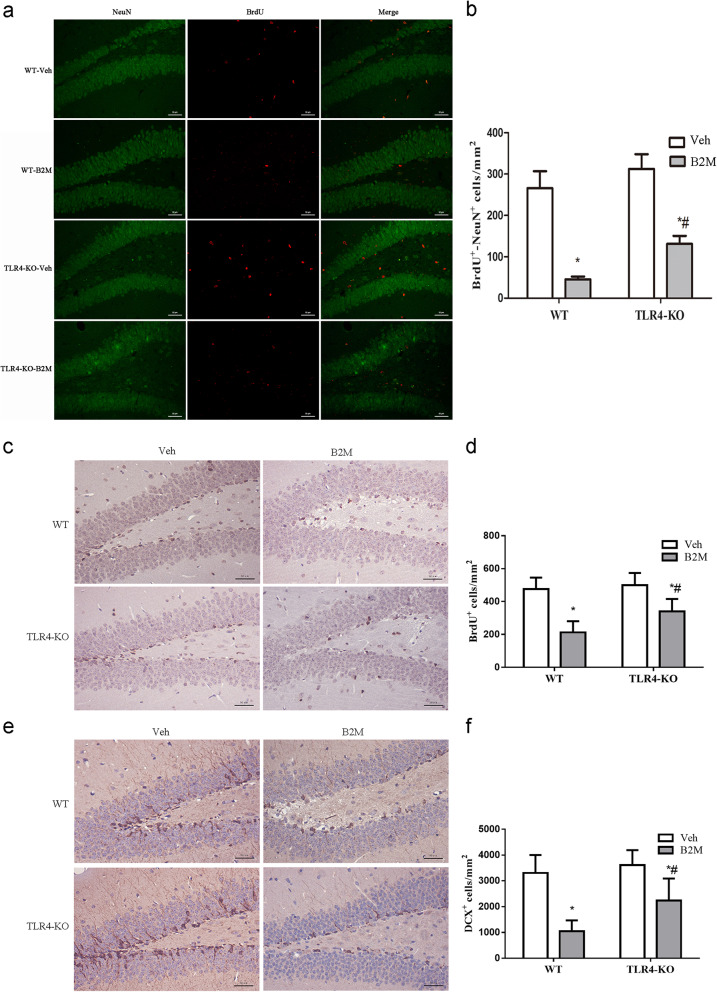
Fig. 3.
TLR4 elimination increases adult hippocampus neurogenesis following B2M treatment. The mature neurons (a), proliferating progenitor cell (c) and immature neurons (e) were assessed in the hippocampus DG region of all groups of mice (n = 4/subgroup). B2M decreased the number of BrdU/NeuN (b), BrdU (d) and DCX (f) positive cells in hippocampus DG, and which was reversed by TLR4 eliminations. The data were analysed using two-way ANOVAs used Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Values are presented as the means ± SD. Significant differences are expressed as follows: *p < 0.05 compared B2M group vs. Veh group of WT and TLR4-KO mice, #p < 0.05 compared B2M group of TLR4-KO mice vs. WT mice, according to the two-way ANOVA. Original magnification: × 100(a); × 200 (c, e). Scale bar = 50 μm. BrdU = 5-bromo-2′ deoxyuridien, DCX+ = Doublecortin positive cells, PSD-95 = postsynaptic density protein 95, WT = wild type C57BL/6, TLR4-KO = TLR4 knockout