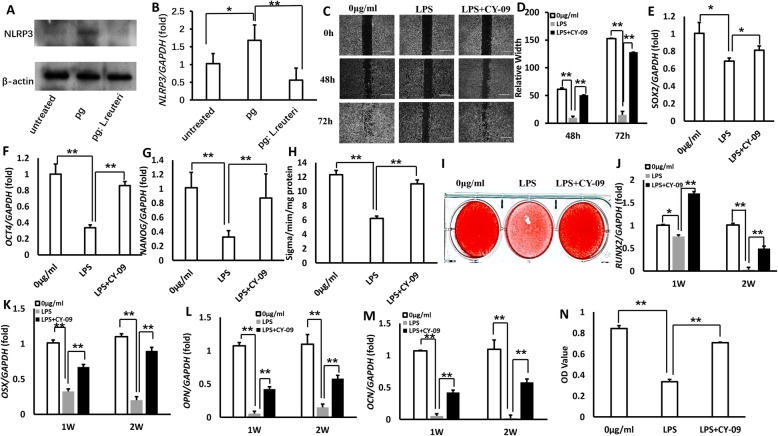
Fig. 6.
LPS increased in P. gingivalis and thereby inhibited the functions of MSCs by activating NLRP3 inflammasome. a, b Western blot and real-time RT-PCR results revealed that NLRP3 expression was significantly increased in palatal tissues from the inoculation of P. gingivalis group compared to the mixture of L. reuteri and P. gingivalis group, and untreated group. β-actin was used as an internal control in western blot assay. c, d The cell migration assay results demonstrated that LPS significantly inhibited GMSC migration, and NLRP3 inhibitor CY-09 rescued the capacity of GMSC migration after LPS treatment. e–g Real-time RT-PCR results showed that LPS inhibited the expression of SOX2, OCT4, and NANOG, and CY-09 restored the capacities of MSCs. h, i ALP activity assay and alizarin red staining assay. j-m Real-time RT-PCR results further testified that NLRP3 activation inhibited the expression of the crucial transcription factors for modulating osteogenic differentiation: RUX2, OSX, OPN, and OCN, and CY-09 rescued the functions of osteogenic differentiation. n Counting kit-8 assay results showed that CY-09 restored the proliferation potential of GMSCs caused by LPS-induced NLRP3 activation. GAPDH was an internal control. Error bars represent SD (n = 3). *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01